TECH
Programming Logic Training for Beginners

Programming logic is the foundation of all coding it’s your ability to think computationally and break down complex problems into clear, executable steps. Think of it this way: if programming languages are different spoken languages, then programming logic is the universal story you’re trying to tell. The logic is the narrative, and the code is simply the language it’s written in.
This skill, often called computational thinking or algorithmic thinking, is what separates someone who can copy code from tutorials and someone who can build real solutions. When you master programming logic, you develop problem-solving skills that extend far beyond coding. You learn to approach challenges methodically, anticipate edge cases, and design elegant solutions.
The benefits are transformative. Strong logical thinking builds coding confidence, allowing you to tackle projects without constant hand-holding. It enables you to learn new programming languages faster because you already understand the underlying patterns. Whether you’re a student working on school projects, a beginner taking your first steps into tech, or a career-changer building a new skill set, programming logic is your gateway to becoming a true programmer rather than just a code copier.
The 5 Pillars of Programming Logic: Core Concepts Explained
Before diving into your training roadmap, you need to understand the fundamental building blocks that form the basis of all programs. These five pillars appear in every programming language, from Python to JavaScript to C++.
1. Variables & Data Types: The Memory Boxes
Variables are named containers that store information your program needs to remember. Think of them as labeled boxes in a warehouse—each box has a name and holds a specific type of item.
Real-world analogy: When you save a contact in your phone, “John Smith” is stored in a variable called contactName, and his phone number “555-1234” might be in phoneNumber.
Pseudocode example:
SET playerName TO "Alex"
SET playerScore TO 0
SET isGameActive TO trueData types define what kind of information each variable holds: text (strings), numbers (integers or decimals), true/false values (booleans), and more. Understanding data types helps you avoid logic errors like trying to do math with words.

2. Conditional Logic (If/Else): The Decision Points
Conditional statements are how your program makes decisions based on different situations. They’re the branching paths that make programs interactive and responsive.
Real-world analogy: “If it’s raining, take an umbrella. Otherwise, wear sunglasses.”
Pseudocode example:
IF age >= 18 THEN
PRINT "You can vote"
ELSE
PRINT "You're not old enough to vote yet"
END IFConditionals use comparison operators (greater than, less than, equals) and logical operators (AND, OR, NOT) to evaluate conditions. Mastering these is crucial for creating programs that behave differently based on user input or changing conditions.
3. Loops: The Power of Automation
Loops allow you to repeat actions without writing the same code multiple times. They’re the secret to processing large amounts of data and automating repetitive tasks.
Real-world analogy: “For each item in your shopping cart, scan the barcode and add the price to your total.”
Pseudocode example:
SET counter TO 1
WHILE counter <= 10 DO
PRINT counter
SET counter TO counter + 1
END WHILEThe two main types are for loops (when you know how many times to repeat) and while loops (when you repeat until a condition changes). Understanding when to use each type is a key logic skill.
4. Functions: Your Code’s Building Blocks
Functions are reusable blocks of code that perform specific tasks. They help you organize your program, avoid repetition, and make your code easier to understand and maintain.
Real-world analogy: A recipe is like a function—you can call “make pancakes” whenever you want breakfast instead of remembering all the steps each time.
Pseudocode example:
FUNCTION calculateArea(length, width)
SET area TO length * width
RETURN area
END FUNCTION
SET roomArea TO calculateArea(12, 10)
PRINT roomArea // Outputs: 120Functions accept inputs (parameters), process them, and often return outputs. Learning to break your programs into well-designed functions is a mark of advancing logical thinking.
5. Data Structures: Organizing Your Information
Data structures are specialized ways to organize and store collections of data. The most common beginner-friendly structure is the array (or list)—an ordered collection of items.
Real-world analogy: A playlist is a list of songs, a to-do list is a list of tasks, your email inbox is a list of messages.
Pseudocode example:
SET groceryList TO ["milk", "eggs", "bread", "cheese"]
PRINT groceryList[0] // Outputs: "milk"
FOR EACH item IN groceryList DO
PRINT "Buy: " + item
END FORAs you advance, you’ll learn about dictionaries/objects (key-value pairs), sets, and more complex structures. For now, understanding how to store and access collections of related data is essential.
Your Programming Logic Training Plan: A 4-Phase Roadmap
Here’s where theory meets practice. This structured 12-week roadmap takes you from complete beginner to someone who can design and implement real projects with confidence. Each phase builds on the previous one, ensuring you develop strong foundations before advancing.
Phase 1: Foundation (Weeks 1-2): Pseudocode & Flowcharts
Goal: Learn to express logic without worrying about syntax.
Start by solving everyday problems on paper before touching any code. This phase trains your brain to think algorithmically without the distraction of programming language rules.
Key Activities:
- Write pseudocode for daily routines: How do you make coffee? Check your email? Choose what to wear based on weather? Write these as step-by-step instructions with IF statements and loops.
- Draw flowcharts for simple decisions: Use flowchart symbols (rectangles for processes, diamonds for decisions) to map out logic visually. Try flowcharting how an ATM decides whether to dispense cash.
- Practice decomposition: Take a complex task like “plan a birthday party” and break it into smaller subtasks. Then break those down further until each step is simple and actionable.
Practice Exercise: Write pseudocode for a program that helps someone decide what to eat for dinner based on: available ingredients, dietary restrictions, cooking time available, and number of people to serve.
Phase 2: Application (Weeks 3-6): Master the Building Blocks with Mini-Projects
Goal: Apply each of the 5 pillars through hands-on coding exercises.
Choose one beginner-friendly language (Python, JavaScript, or Ruby are excellent choices) and start translating your pseudocode into real code. Focus on one concept at a time.
Week 3-4: Variables, Data Types & Input/Output
- Project 1: Build a “Personal Info Collector” that asks for name, age, favorite color, and displays a personalized message.
- Project 2: Create a “Tip Calculator” that takes a bill amount and tip percentage, then calculates and displays the total.
Week 4-5: Conditional Logic
- Project 3: Build a “Grade Calculator” that converts numerical scores (0-100) into letter grades (A, B, C, D, F) with appropriate ranges.
- Project 4: Create a “Temperature Advisor” that suggests clothing based on temperature input (if cold, wear a coat; if hot, shorts and t-shirt, etc.).
Week 5-6: Loops
- Project 5: Build a “Multiplication Table Generator” that displays the times table for any number the user enters.
- Project 6: Create a “Number Guessing Game” where the computer picks a random number and the user has multiple attempts to guess it, with “higher” or “lower” hints.
Week 6: Functions & Code Organization
- Project 7: Refactor your previous projects to use functions. For example, turn your tip calculator into a function that can be called multiple times for different bills.
Phase 3: Debugging & Optimization (Weeks 7-8): Thinking Like a Detective
Goal: Develop systematic debugging skills to identify and fix logic errors.
This phase addresses a critical gap in most beginner resources. Understanding the difference between syntax errors (which the computer flags) and logic errors (which produce wrong results) is essential.
Key Debugging Techniques:
1. The Print Statement Method Insert print statements throughout your code to see what’s happening at each step. This helps you track variable values and identify where your logic goes wrong.
2. The Rubber Duck Technique Explain your code line-by-line to an inanimate object (or patient friend). Often, articulating your logic out loud reveals flaws you couldn’t see while reading silently.
3. Isolate the Problem Comment out sections of code to narrow down where the error occurs. Test individual functions separately before testing them together.
4. Check Your Assumptions Logic errors often stem from incorrect assumptions. Does the user always enter a positive number? What if the list is empty? Test edge cases deliberately.
Practice Exercise: Debug intentionally broken code samples. Create a program that should calculate the average of five numbers but has a logic error (like dividing by 4 instead of 5, or not initializing the sum variable correctly). Practice finding and fixing these issues.
Week 8 Challenge: Revisit all your mini-projects from Phase 2. Add input validation (what happens if someone enters text instead of a number?) and error handling. Make your programs bulletproof.
Phase 4: Real-World Synthesis (Weeks 9-12): Capstone Project Build
Goal: Combine all five pillars into a complete, functional program.
Choose one capstone project that interests you. Spend these final weeks designing, building, debugging, and refining it. This project should demonstrate your mastery of programming logic.

Beginner-Friendly Capstone Project Ideas:
1. To-Do List Application
- Store tasks in a list (data structures)
- Add, remove, and mark tasks as complete (functions)
- Display tasks differently based on status (conditional logic)
- Process multiple tasks (loops)
- Save user preferences like name (variables)
2. Quiz Game
- Store questions and answers in data structures
- Track score with variables
- Use loops to present questions one-by-one
- Evaluate answers with conditional logic
- Create functions for displaying questions, checking answers, and showing final results
3. Simple Budget Tracker
- Input income and expenses (variables and data types)
- Categorize expenses using data structures
- Calculate totals and remaining budget (functions)
- Warn if overspending (conditional logic)
- Process multiple transactions (loops)
4. Text-Based Adventure Game
- Create a story with branching paths (conditional logic)
- Track player inventory and health (variables and data structures)
- Implement game loop (loops)
- Design reusable encounter functions (functions)
- Handle player choices and outcomes (comprehensive logic)
Development Approach:
- Week 9: Write detailed pseudocode for your entire project. Draw flowcharts for complex parts.
- Week 10: Build the minimum viable version—get basic functionality working first.
- Week 11: Add features, improve user experience, handle edge cases.
- Week 12: Debug thoroughly, refactor messy code, add comments explaining your logic.
Top Resources & Tools for Effective Practice
Success in programming logic training requires the right resources at the right time. Here’s a curated list organized by your learning phase.
Interactive Learning Platforms
freeCodeCamp — Excellent for Phase 1-2. Their JavaScript curriculum emphasizes logical thinking with immediate feedback. Completely free with a supportive community.
Codecademy — Great for Phase 2-3. Their interactive environment lets you write code in the browser with hints and explanations. The free tier covers fundamentals well.
Scrimba — Perfect for visual learners. Screencasts you can pause and edit make it easy to experiment with examples as you learn.
Logic & Algorithm Challenges
HackerRank — Start with their “Interview Preparation Kit” beginner tracks during Phase 3. They break problems into difficulty levels and provide hints.
Edabit — Specifically designed for beginners, with very easy challenges to build confidence before moving to harder problems.
LeetCode Explore Cards — Use their “Arrays 101” and “Recursion I” courses during Phase 4 to advance your problem-solving patterns.
Codewars — Gamified coding challenges with a leveling system. Start at 8 kyu (easiest) and work your way up.
Communities for Support
Stack Overflow — The world’s largest Q&A site for programmers. Search before asking—chances are your question has been answered. Learn to ask good questions by being specific about your problem.
Reddit r/learnprogramming — Supportive community for beginners. Weekly threads for questions, motivation, and sharing progress. Great for when you feel stuck or discouraged.
Discord Coding Communities — Real-time chat with other learners. Look for communities specific to your chosen language (The Programmer’s Hangout, Python Discord, etc.).
GitHub — Not just for code storage. Reading others’ beginner projects teaches you different approaches to solving problems. See how real code is structured and organized.
Advanced Tips: Moving From Beginner to Intermediate Logical Thinking
Once you’ve completed the 12-week roadmap, these strategies will help you continue advancing your logical thinking skills.
How to Read and Analyze Others’ Code
Reading code is a different skill from writing it—and it’s equally important. Start with well-commented beginner projects on GitHub. Ask yourself:
- What problem is this code solving?
- How is the logic organized into functions?
- What edge cases are being handled?
- Could this be written more efficiently?
- What naming conventions does the author use?
Try the “code reading club” approach: pick one interesting open-source project each month and spend 30 minutes reading through its codebase. Document what you learn about logic patterns and code organization.
Introduction to Time & Space Complexity (Big O Basics)
As you advance, you’ll learn that some solutions are more efficient than others. Big O notation describes how your program’s performance scales as input grows.
Simple example: Searching through a list one item at a time is O(n)—it takes longer with bigger lists. Using a binary search on a sorted list is O(log n)—much faster. A nested loop checking every pair is O(n²)—slow with large datasets.
You don’t need to master this as a beginner, but awareness helps you start thinking about efficiency. When you write a loop inside another loop, ask yourself: “Will this become too slow with 1,000 items? 10,000?”
The Role of Programming Paradigms (OOP vs. Functional)
Different programming paradigms are different ways of organizing logic:
Procedural Programming (what you’ve learned so far) organizes code as a sequence of procedures or functions. Good for straightforward problems.
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) bundles related data and functions into “objects” that model real-world entities. Excellent for complex systems with many interacting parts.
Functional Programming treats computation as evaluating mathematical functions, avoiding changing state. Leads to predictable, testable code.
As an intermediate learner, start exploring OOP concepts like classes, objects, inheritance, and encapsulation. These paradigms don’t replace logic fundamentals—they provide new ways to organize and express your logical thinking at scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to build good programming logic?
It varies by individual, but with consistent practice using a structured roadmap like this one, most people grasp the fundamentals in 2-3 months. The key word is “consistent”—daily practice for 30-60 minutes beats weekend cramming. You’ll notice logical thinking improving in everyday life too, not just in coding. True mastery develops over years, but you’ll be comfortable building real projects within 3-6 months of dedicated practice.
Can I learn programming logic without knowing a programming language?
Absolutely! In fact, starting with pseudocode and flowcharts (Phase 1 of this roadmap) is the recommended approach. It lets you focus purely on logical thinking without the frustration of syntax errors and language-specific quirks. Many computer science courses teach algorithmic thinking before any actual coding. Once your logic is solid, picking up language syntax becomes much easier—you’re just learning new vocabulary for ideas you already understand.
What’s the difference between a syntax error and a logic error?
A syntax error is like a spelling or grammar mistake—the computer doesn’t understand what you’re trying to say, so it refuses to run your code. Examples: forgetting a closing parenthesis, misspelling a keyword like “print,” or using the wrong indentation.
A logic error is more subtle and dangerous. Your code runs without errors, but produces incorrect results because your instructions are wrong. Example: calculating tax as price * 0.8 instead of price * 0.08, or using <= when you meant <. The program executes perfectly—it’s just solving the wrong problem. Debugging logic errors requires systematic thinking and testing, which is why Phase 3 of the roadmap focuses on this skill.
I understand the concepts but get stuck when building projects. What should I do?
This is extremely common and indicates you’re at a crucial growth point. Here’s a proven unsticking process:
- Go back to breaking down the problem. Write the project requirements as a bulleted list, then break each bullet into smaller steps.
- Write pseudocode for each step before touching actual code.
- Build the simplest possible version first—ignore nice-to-have features.
- When stuck on a specific part, search for similar examples. If building a tip calculator, search “simple calculator tutorial” to see the pattern, then adapt it.
- Take breaks. Your subconscious often solves problems while you’re away from the keyboard.
Remember: getting stuck is part of the learning process, not a sign you can’t do this. Every programmer, from beginner to senior, gets stuck regularly. The difference is they’ve developed debugging and problem-decomposition skills through experience—skills you’re building right now.
Are strong math skills required for programming logic?
Not necessarily. While mathematics involves logical reasoning, programming logic is more about structured, step-by-step problem-solving than advanced math. Most programming requires basic arithmetic (addition, multiplication, percentages) and understanding of comparisons (greater than, less than).
The overlap is in logical reasoning—if you can follow “if this, then that” reasoning and understand cause and effect, you have what you need. Fields like game development, data science, and graphics programming use more advanced math, but general software development focuses on business logic, data manipulation, and user interactions—areas where organized thinking matters more than calculus.
TECH
Kibard: Uncovering Its Dual Meaning – From Ancient Artifact to Modern Keyboard

Kibard into a search engine Thousands of people search for this word every month. But here is what makes ‘kibard’ genuinely fascinating: it carries two completely different meanings that are rarely acknowledged in a single place.
On one hand, ‘Kibard’ refers to a historical artifact an ancient object of cultural significance, steeped in symbolism, heritage, and ritual. On the other hand, ‘kibard’ is one of the most widely used phonetic spellings of the word ‘keyboard,’ particularly among non-native English speakers or those who rely on voice search.
This guide is designed to be the definitive resource on both. Whether you arrived here seeking the history of the Kibard artifact or simply looking for information about a keyboard, you will find clear, thorough, and practical answers below.
What Does “Kibard” Mean? Solving the Mystery
The confusion around ‘kibard’ stems from the fact that it exists in two separate worlds: the world of ancient culture and the world of everyday technology. Let us explore each in detail.
Definition 1: The Kibard as a Historical Artifact
History and Origins of the Kibard
The Kibard, in its historical context, is an artifact that traces its roots to ancient civilizations. Discovered across a number of early societies, the Kibard was not simply a decorative object it was a purposeful creation that held deep meaning for the people who made and used it.
Crafted with extraordinary skill, the Kibard was considered a mark of status and identity. Those who possessed one were often leaders, spiritual figures, or master artisans. Its creation required specialized knowledge passed down through generations, making each Kibard a unique expression of the cultural knowledge and craftsmanship of its time.
Archaeologists and historians who have studied the Kibard note its consistent appearance across geographically distant cultures, suggesting that either its concept spread through ancient trade routes or arose independently in multiple societies a testament to its universal significance.
The Cultural Significance and Symbolism of the Kibard
Beyond its physical form, the Kibard was rich in symbolic meaning. It was commonly used in rituals, celebrations, and rites of passage. Communities treated the Kibard as a bridge between the earthly and the spiritual a physical object that carried intangible power.
In many cultures, the Kibard served as a storytelling tool. Elders and leaders used it to pass down oral histories, moral lessons, and community values to younger generations. Its presence in a gathering was a signal that what was being shared was of great importance.
The Kibard was also a cherished heirloom. Families passed it down through generations, viewing it as a vessel of ancestral memory and identity. Some cultures believed the Kibard offered protection to its holder, reinforcing its spiritual role within the community.
Definition 2: The Kibard as a Modern Keyboard
Why Do People Search for “Kibard”? The Phonetic Spelling Explained
In the modern digital world, ‘kibard’ has taken on a second life as a commonly used phonetic alternative to the word ‘keyboard.’ When people say ‘keyboard’ naturally and quickly particularly those whose first language is not English it often sounds like ‘kibard.’
With the rise of voice-to-text technology and voice search on smartphones, people frequently speak search queries aloud. The device interprets the spoken word ‘keyboard’ and types what it hears which is often ‘kibard.’ As a result, ‘kibard’ has become one of the most searched misspellings on the internet.
The important thing to understand is this: there is no difference in what the user is looking for. Whether someone types ‘kibard’ or ‘keyboard,’ they are seeking the same product and the same information.
What is a Keyboard? A Simple Explanation for Beginners
A keyboard or kibard, as it is phonetically known is one of the most essential input devices for any computer, laptop, tablet, or smartphone. Its primary function is to allow a user to enter text, numbers, and commands by pressing individual keys.
Each key on a keyboard sends a unique electronic signal to the connected device, which interprets that signal as a specific character, number, or function. The keyboard has remained a fundamental piece of technology for over a century, evolving from mechanical typewriters to the slim, wireless, and even touch-based devices we use today.
Exploring the Modern Kibard (Keyboard): A Complete Guide
Different Types of Keyboards (Kibards) for Every Need
Not all keyboards are the same. Depending on how you intend to use your kibard, different types will serve different purposes. Here is a breakdown of the most common types available today:
Mechanical Keyboards
Mechanical keyboards are the preferred choice of gamers, programmers, and writers who spend long hours typing. Each key has its own individual mechanical switch, which provides a satisfying tactile bump and, in some models, an audible click with every keystroke.
The benefits of a mechanical kibard include excellent durability (rated for tens of millions of keystrokes), highly customizable keycaps, and a typing experience that many users find more comfortable and accurate over extended periods. Popular switch types include linear, tactile, and clicky variants, each offering a different feel and sound profile.
Membrane Keyboards
Membrane keyboards are the most common type found in offices and homes. Instead of individual switches, they use a soft, pressure-sensitive membrane beneath the keys. When a key is pressed, it pushes down on this membrane to register a keystroke.
Membrane kibards are generally quieter, more affordable, and lighter than mechanical ones. They are an excellent choice for office environments, general home use, and situations where noise is a concern. The downside is that they tend to have less tactile feedback and a shorter lifespan compared to mechanical keyboards.
Wireless vs. Wired Keyboards
The debate between wireless and wired keyboards comes down to freedom versus reliability. A wireless kibard connects to your device via Bluetooth or a 2.4 GHz USB receiver, allowing you to position it anywhere on your desk without being limited by cable length. This makes for a cleaner, more organized workspace.
A wired kibard, on the other hand, requires no charging and has zero chance of signal interference or connection drops. For professional gamers and those who need absolute, uninterrupted performance, a wired keyboard remains the gold standard.
Virtual Keyboards
A virtual keyboard the on-screen kibard on your smartphone or tablet has become the primary typing interface for billions of people worldwide. Modern virtual keyboards are powered by artificial intelligence, offering predictive text, auto-correct, and swipe-to-type features that dramatically improve typing speed and accuracy on touchscreens.
Leading virtual keyboard applications have integrated language models that learn from your typing patterns over time, personalizing the autocomplete suggestions to match your vocabulary and communication style.

Key Features and Specifications to Consider
When choosing a keyboard, several technical specifications will determine how well it suits your specific needs:
- Key Switches: The mechanism under each key. Linear switches are smooth; tactile switches have a bump; clicky switches make an audible sound.
- Backlighting and RGB: Many modern keyboards offer adjustable backlighting, with RGB keyboards providing millions of color options for customization and aesthetics.
- Connectivity: USB-C wired connections offer reliability, while Bluetooth and 2.4 GHz wireless connections offer freedom and flexibility.
- Battery Life: For wireless keyboards, battery life ranges from a few weeks to several months depending on the model and usage.
- Form Factor: Full-size keyboards include a number pad; tenkeyless (TKL) models remove the number pad for a more compact layout; 60% keyboards remove even more keys for maximum portability.
- Rollover and Anti-Ghosting: These features determine how many keys can be pressed simultaneously and accurately registered important for gaming.
How to Use a Keyboard More Effectively
Essential Keyboard Shortcuts for Productivity
One of the most powerful ways to increase your efficiency is to master keyboard shortcuts. These combinations of keys allow you to perform common tasks without ever touching the mouse, saving significant time throughout your workday:
- Ctrl + C / Cmd + C: Copy selected text or files
- Ctrl + V / Cmd + V: Paste copied content
- Ctrl + Z / Cmd + Z: Undo the last action
- Ctrl + S / Cmd + S: Save the current file
- Alt + Tab / Cmd + Tab: Switch between open applications
- Ctrl + F / Cmd + F: Open the search bar in a document or browser
- Windows Key + D / Mission Control: Show the desktop or all open windows
Tips to Improve Your Typing Speed and Accuracy
Whether you call it a kibard or a keyboard, using it effectively is a skill that improves with practice. Here are proven strategies for becoming a faster, more accurate typist:
- Use all ten fingers and practice touch typing typing without looking at the keys.
- Sit with your back straight, elbows at a 90-degree angle, and wrists relaxed above the keyboard.
- Practice with dedicated typing tutorial websites or apps that give you real-time feedback on speed and accuracy.
- Start slowly and focus on accuracy. Speed will naturally increase as muscle memory develops.
- Take regular breaks to avoid repetitive strain injury, especially during long typing sessions.
Understanding Keyboard Layouts (QWERTY, AZERTY, and Others)
The layout of a keyboard the arrangement of its keys varies depending on the language and region for which it was designed. The most widely used layout globally is QWERTY, named for the first six letters on the top-left row of letter keys. It was designed in the 1870s for typewriters.
French-speaking countries commonly use AZERTY, German-speaking countries use QWERTZ, and many other specialized layouts exist for different languages and scripts. Choosing the right layout for your language ensures you can type efficiently without remapping keys or using workarounds.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Your Kibard
How to Clean Your Keyboard Safely
Regular cleaning extends the life of your keyboard and keeps it hygienic. Keyboards are among the dirtiest surfaces in any workspace, collecting dust, crumbs, and bacteria over time. Here is a safe, step-by-step cleaning guide:
- Step 1: Unplug the keyboard (or turn it off if wireless) before cleaning.
- Step 2: Turn it upside down and gently shake it to dislodge loose crumbs and debris.
- Step 3: Use a can of compressed air to blow out particles from between the keys, working in short bursts.
- Step 4: Lightly dampen a lint-free microfiber cloth with isopropyl alcohol and gently wipe the tops of the keycaps.
- Step 5: For deeper cleaning, you can remove the keycaps (on mechanical keyboards) and wash them in warm soapy water, then let them dry completely before reattaching.
- Step 6: Allow everything to dry fully before reconnecting or powering on.
Common Keyboard Problems and Fixes
Even the best keyboard can experience issues. Here are the most common problems and how to solve them:
Keys Not Responding: Try cleaning under the affected keys first. If the problem persists, update your keyboard driver via Device Manager (Windows) or System Preferences (Mac). For wireless keyboards, re-pair the device.
Wrong Characters Being Typed: This is usually a keyboard layout issue. Go to your operating system settings and verify that the correct language input is selected.
Wireless Keyboard Disconnecting: Replace or charge the battery, ensure there is no interference from other wireless devices, and try moving the USB receiver to a different port closer to the keyboard.
Keys Sticking: This is typically caused by liquid or debris under the keycap. Remove the keycap, clean underneath with isopropyl alcohol on a cotton swab, and allow it to dry fully before replacing.
The Kibard as an Artifact: Bringing History into the Modern Day
The historical Kibard is not merely a museum piece. In fact, there is a growing movement to bring ancient artifacts like the Kibard back into daily life not as objects of superstition, but as tools for wellness, artistic expression, and cultural education.

Modern Uses of the Historical Kibard
In Wellness and Mindfulness
Many wellness practitioners and mindfulness teachers have incorporated historically significant objects like the Kibard into their practices. Its ancient craftsmanship and cultural weight make it a powerful focal point for meditation. Holding or contemplating the Kibard serves as an anchor to the present moment, drawing the mind away from distractions and toward a sense of timeless connection.
The ritual of engaging with a meaningful object is a well-documented mindfulness technique. By introducing the Kibard into this context, practitioners connect the modern practice of meditation with its ancient roots in ritual and ceremony.
In Art and Home Decor
The unique aesthetic of a Kibard shaped by ancient craftsmanship makes it a compelling addition to contemporary interior design. Art collectors and interior designers are increasingly interested in authentic artifacts that tell a story. A Kibard displayed in a home or studio becomes an instant conversation piece, inviting curiosity and discussion about its origins and meaning.
It can be paired with modern decor to create a striking contrast between ancient tradition and contemporary style, or displayed in a dedicated cultural corner alongside other heritage objects.
As an Educational Tool
Schools, museums, and cultural organizations have found real value in using the Kibard as an educational tool. The object provides a tangible connection to history that textbooks alone cannot offer. Students who can see and study an artifact engage more deeply with the history and culture it represents.
The Kibard can serve as a starting point for discussions about trade routes, cultural exchange, craftsmanship, and the universal human desire to create meaningful objects. It bridges the gap between academic history and lived human experience.
Debunking Common Myths and Misconceptions about the Kibard
Over time, both definitions of ‘kibard’ have attracted their share of myths. Let us address the most common misconceptions:
Myth 1: The Kibard (artifact) is just a decorative item with no deeper purpose. This is incorrect. The historical Kibard was a functional, meaningful object within its cultural context, used in rituals, storytelling, and as a symbol of identity.
Myth 2: You need special skills to use a Kibard (keyboard). Not at all. While advanced keyboard skills take practice, anyone can begin using a keyboard with no prior experience. The basic functions are intuitive.
Myth 3: The Kibard’s power or significance diminishes over time. For the artifact, significance grows over time as it accumulates history and meaning. For the keyboard, newer models regularly improve on older ones, but older keyboards rarely ‘stop working’ from age alone.
Myth 4: The Kibard is tied to only one culture. The historical Kibard, in its various forms, has been found across multiple ancient cultures. It is a globally shared concept, not the exclusive property of any single tradition.
Frequently Asked Questions About Kibard
The following questions are among the most commonly searched queries related to ‘kibard.’ This FAQ section is designed to provide clear, direct answers.
Is ‘kibard’ a real word?
While ‘kibard’ does not appear in standard dictionaries as a formal entry, it is widely recognized as a phonetic spelling of ‘keyboard’ and is a legitimate search term with clear user intent. In the cultural/historical sense, ‘Kibard’ refers to a specific type of ancient artifact.
What is the difference between a Kibard and a keyboard?
When referring to technology, there is no difference. ‘Kibard’ is simply a common misspelling or voice-typed version of ‘keyboard,’ the input device used with computers and mobile devices.
What is a Kibard in history?
Historically, a Kibard refers to a type of artifact from ancient cultures, associated with craftsmanship, social status, spirituality, and ritual. It was used in ceremonies, as a storytelling tool, and as a symbol of identity.
Why is a keyboard sometimes called a Kibard?
The term ‘kibard’ arises from how ‘keyboard’ sounds when spoken quickly or with certain accents. Voice search technology often transcribes the spoken word ‘keyboard’ as ‘kibard,’ which has spread the usage of this phonetic spelling online.
What are the best Kibards for long typing sessions?
For long typing sessions, mechanical keyboards are widely recommended due to their tactile feedback, ergonomic design options, and high durability. Membrane keyboards are a quieter, more affordable alternative suitable for general office use.
How do I clean my Kibard?
Unplug or power off your keyboard. Shake it gently to remove loose debris, then use compressed air between the keys. Wipe the keycap surfaces with a lightly dampened lint-free cloth. For deeper cleaning, remove the keycaps (if possible) and wash them separately. Let everything dry completely before use.
Can I use a wireless Kibard for gaming?
Yes. Modern wireless keyboards have very low latency and are suitable for most gaming scenarios. Competitive professional gamers may still prefer wired connections for absolute zero latency, but the difference for casual and intermediate gaming is minimal.
What is a mechanical Kibard?
A mechanical keyboard uses individual physical switches under each key, providing distinct tactile feedback and, in many models, an audible click. Mechanical keyboards are valued for their precision, customizability, and longevity compared to membrane alternatives.
Kibard at a Glance: Quick Comparison Table
The table below summarizes the two primary meanings of ‘kibard’ for quick reference:
| Feature | Kibard (Historical Artifact) | Kibard (Modern Keyboard) |
| Category | Cultural Heritage / Archaeology | Consumer Technology |
| Primary Use | Ritual, ceremony, storytelling, status symbol | Text input, navigation, productivity |
| Materials | Stone, bone, metal, wood (varies by culture) | Plastic, metal, rubber, glass (virtual) |
| Who Uses It | Spiritual leaders, community figures, collectors | Everyone with a computer or smartphone |
| Modern Relevance | Wellness, art, education, decor | Office work, gaming, communication |
| Availability | Museums, antique markets, cultural collections | Electronics stores, online retailers |
Conclusion
The word ‘kibard’ is a reminder of how language, technology, and culture intersect in unexpected ways. Whether you arrived here looking for an ancient artifact steeped in cultural symbolism or simply searching for the right keyboard for your work and lifestyle, we hope this guide has served as the clearest, most complete resource available.
If you are drawn to the historical Kibard, consider exploring it through the lens of wellness, art, or education. If it is the modern keyboard you are seeking, use this guide to match the right type mechanical, membrane, wireless, or virtual to your specific needs and budget.
Both versions of the Kibard share something important: they are tools for expression, communication, and connection. One bridges the past to the present through craftsmanship and ritual. The other bridges people to one another through the everyday act of typing.
TECH
Platform Event Trap (PET) Guide: From Hardware Alerts to Ransomware Defense

In the modern data center, most monitoring tools watch the operating system but attackers and hardware failures don’t always play by the OS’s rules. Platform Event Traps (PETs) operate below the software stack, at the firmware and hardware level, providing a critical layer of visibility that traditional endpoint detection tools simply cannot reach. This guide covers what PETs are, how they work, how to configure them, and why they are becoming indispensable in modern cybersecurity operations.
What is a Platform Event Trap (PET)? Defining the Technology
A Platform Event Trap is a network notification mechanism defined by the Alert Standard Format (ASF) and Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) specifications. When a hardware component on a server such as the CPU, power supply, chassis, or BIOS experiences a notable condition, it signals the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC). The BMC encapsulates this event into an SNMP Trap packet and transmits it via UDP (typically port 162) to a pre-configured management console, entirely independent of the server’s operating system.
In plain terms: even if a server’s OS is crashed, compromised, or powered down, PET can still fire an alert. This is the defining characteristic that makes it valuable for both infrastructure reliability and advanced security monitoring.
PET vs. Standard Software Logs: Why Hardware Context Matters
Traditional logging (syslog, Windows Event Log, EDR telemetry) depends on the OS being functional and trustworthy. A sufficiently sophisticated attacker or a simple kernel panic can silence those channels entirely. PET operates through the BMC, which has its own processor, memory, and network interface, forming an independent “out-of-band” management channel.
Consider these scenarios where PET catches what software misses:
- A UEFI rootkit modifies BIOS settings during a late-night maintenance window. The OS sees nothing unusual. PET fires an “Unauthorized BIOS Change” alert immediately.
- A server case is physically opened in a co-location facility. No software-level alert triggers. PET detects the chassis intrusion microsensor and alerts the SOC.
- Firmware-level ransomware attempts to persist by writing to the UEFI partition. PET captures the firmware tamper event before the OS has even loaded.
Core Architecture: How Platform Event Traps Work
Understanding the PET lifecycle helps engineers configure, troubleshoot, and tune alert pipelines effectively. The flow from hardware event to actionable alert passes through four stages:
- Hardware Event Trigger: A physical or logical condition threshold is crossed (temperature, voltage, fan speed, intrusion sensor, etc.).
- BMC/IPMI Capture: The BMC detects the event via its sensors and internal event log. It identifies the event category and severity.
- SNMP Encapsulation: The BMC wraps the event data into an SNMP Trap PDU (Protocol Data Unit), embedding the Object Identifier (OID), varbinds (variable bindings with event metadata), and community string or SNMPv3 credentials.
- UDP Transmission: The trap is sent via UDP to the management console (port 162 by default). UDP is used because it is lightweight and does not require a connection critical in failure scenarios.
Events vs. Alarms: Understanding the Difference
Many engineers use “event” and “alarm” interchangeably, but the distinction is important for building an effective alert pipeline.
An Event Trap is a single, stateless notification it fires once and carries no “resolved” counterpart. Examples include a power cycle or a one-time chassis intrusion. An Alarm Trap, by contrast, is a paired notification system: one trap is sent when an issue becomes Active (e.g., temperature exceeds threshold) and a corresponding Cleared trap is sent when the issue resolves. Without understanding this distinction, a SOC analyst might see hundreds of duplicate “temperature high” events and have no way to know whether the problem is ongoing or resolved.
| Trap Type | State | Paired? | Example |
| Event Trap | One-shot | No | Chassis intrusion, Power cycle |
| Alarm Trap (Active) | Ongoing problem | Yes | CPU temp > 85°C |
| Alarm Trap (Cleared) | Problem resolved | Yes | CPU temp returned to normal |
The Role of the Trap Aggregator (e.g., Trapd)
In environments with dozens or hundreds of servers, raw traps flowing directly to a SIEM can create noise and performance problems. A Trap Aggregator (such as Oracle’s Trapd service) acts as an intelligent middleware layer. Its key functions include:
- De-duplication: Suppressing repeated identical traps within a configurable time window.
- Rules-based Filtering: Using a BaseRules file and LoadRules definitions to categorize and route traps based on OID, source IP, or severity.
- Normalization: Converting raw SNMP varbinds into structured log formats compatible with SIEM ingestion.
- Bulk Insert: Batching high-volume trap data for efficient database writes, preventing pipeline bottlenecks.

Configuring Platform Event Traps: A Vendor-Agnostic Guide
Configuration involves three layers: enabling PET at the firmware level, setting the destination for trap delivery, and tuning the traps themselves at the CLI or management interface.
Step 1: Enabling PET in BIOS/UEFI
PET must first be activated in the server firmware before any traps can be sent. The specific path varies by vendor, but the general procedure is:
- Reboot the server and enter the BIOS/UEFI setup interface (typically F2, Del, or F10 during POST).
- Navigate to the Server Management or IPMI Configuration section.
- Enable the “Platform Event Traps” or “ASF” option.
- Confirm BMC firmware is up to date before enabling (outdated BMC firmware is a common source of malformed traps).
Step 2: Setting Destination Addresses (Management Console IP)
Once PET is enabled, the BMC needs to know where to send traps. There are two configuration approaches:
Manual Configuration: The administrator directly sets the destination IP address of the management console or trap aggregator via the BMC web interface, IPMI tool, or CLI.
Auto-Configuration (ASF Specification): The DMTF ASF standard defines a mechanism where the managed node can receive a “Configuration Packet” from the management console typically delivered via a DHCP vendor option that automatically provisions the trap destination IP, community string, and event filters. This is essential for large-scale, zero-touch data center deployments.
Step 3: CLI Configuration Examples
Cisco SONiC (Data Center Switching Platform):
# Enable a specific trap event with priority and action config platform cisco trap-configuration -e <event_id> -p <priority> -a <action> # Example: Configure a non-compliant multicast event config platform cisco trap-configuration -e LA_EVENT_IPV4_NON_COMP_MC -p 5 -a punt # Actions: # punt = forward trap to CPU for processing # drop = silently discard the event (use for suppression)
Huawei (Enterprise/Carrier Networking):
# Enable SNMP trap sending globally snmp-agent trap enable # Specify trap destination host snmp-agent target-host trap address udp-domain 10.0.1.100 params securityname public
Step 4: SNMPv3 Setup for Secure Traps
SNMPv1 and v2c transmit community strings in plaintext, making them unsuitable for security-sensitive environments. SNMPv3 adds authentication and encryption. The three security levels are:
| Security Level | Authentication | Encryption | Use Case |
| noAuthNoPriv | None | None | Internal test environments only |
| authNoPriv | MD5 or SHA | None | Integrity-verified, not encrypted |
| authPriv | MD5 or SHA | DES or AES | Production security environments |
Common SNMPv3 configuration errors to watch for:
- authenticationFailure: The AuthPassword configured on the BMC does not match the trap receiver. Verify both sides use the same hash algorithm (SHA-256 recommended over MD5).
- decryptionError: Privacy protocol mismatch (e.g., BMC configured for DES but aggregator expects AES-128). Standardize on AES-256 for new deployments.
- Engine ID Mismatch: Each SNMPv3 entity has a unique Engine ID. A misconfigured Engine ID on either side will silently drop traps verify with an SNMP walk before production deployment.
The Critical Role of PET in Modern Cybersecurity
For years, Platform Event Traps were primarily an infrastructure reliability tool alerting on hardware failures before they caused outages. The modern threat landscape has elevated PET’s importance to a first-class security control. Here is why.
Detecting Firmware-Level Ransomware and Persistence Mechanisms
Advanced ransomware groups and nation-state actors increasingly target firmware as a persistence mechanism. By writing malicious code to UEFI flash storage, attackers can survive OS reinstallation, disk wiping, and even hardware replacement in some configurations. These attacks are invisible to traditional Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools, which operate above the OS kernel.
PET bridges this gap. Because the BMC monitors firmware integrity independently, unauthorized writes to BIOS/UEFI regions trigger hardware-level events that PET can capture and forward to a SIEM. A properly tuned PET pipeline can alert a SOC within seconds of a firmware tamper attempt long before the attacker’s payload executes.
Physical Security Alerts: Chassis Intrusion Detection
Every enterprise-grade server includes a chassis intrusion sensor a microsensor that triggers when the server case is opened. For most organizations, this sensor’s data goes unmonitored. PET changes that: the intrusion event is captured by the BMC and forwarded as a trap to the management console immediately.
This seemingly simple capability has significant security implications for co-location data centers, branch offices, and environments with elevated insider threat risk. A chassis intrusion PET, correlated with after-hours access badge records in a SIEM, becomes a high-confidence indicator of a physical tampering attempt.
Anomaly Detection via Environmental Triggers
Hardware anomalies are often leading indicators of software-based attacks. PET enables correlation between environmental events and security incidents:
- CPU Load Spikes: An unexpected sustained CPU spike on an idle server could indicate crypto-mining malware. A PET thermal alert (CPU temperature rising) can be the first signal.
- Unexpected Power Cycles: Ransomware and destructive malware often force reboots to complete their attack chain. An out-of-schedule power cycle PET, correlated with file system activity logs, can confirm an attack in progress.
- Voltage Fluctuations: Hardware implants or tampering with power delivery can manifest as voltage irregularities detectable by the BMC’s power monitoring.
Integrating PET Alerts into Your Security Stack (SIEM/SOC)
Raw SNMP traps are not immediately consumable by a SOC analyst. An integration pipeline is necessary to transform PET data into actionable intelligence.
Normalizing Trap Data for Correlation
Each PET arrives with an OID (the event type identifier) and varbinds (key-value pairs carrying event metadata such as sensor ID, threshold value, and current reading). The integration pipeline must parse these into normalized log fields.
For Splunk, this typically means a custom props.conf and transforms.conf that extract varbind fields and map them to a common information model (CIM). For Microsoft Sentinel or IBM QRadar, vendor-specific data source mapping files perform the same function. The critical output fields to normalize are: event_type, source_hardware, sensor_id, threshold_value, current_value, severity, and timestamp.
Avoiding Alert Fatigue: Tuning Thresholds and Filters
Alert fatigue is the most common reason PET deployments fail to deliver security value. If a temperature alert fires at 50°C in a data center running at an ambient 35°C, the SOC will learn to ignore it. Tuning is not optional it is the difference between a monitoring tool and a security control.
Recommended tuning principles:
- Set temperature thresholds 10-15°C below the manufacturer’s critical shutdown temperature, not at a fixed default value.
- Suppress recurring identical alerts (de-duplication) using the aggregator’s time-window function. A one-minute de-dup window eliminates 80-90% of alert noise in most environments.
- Create severity tiers: “Info” (log only), “Warning” (ticket creation), “Critical” (page on-call). Map event types to tiers deliberately.
- Suppress expected maintenance events (planned reboots, scheduled firmware updates) using a maintenance window flag in your SIEM.
| Event Type | Recommended Threshold | Severity Tier | SIEM Action |
| CPU Temperature | > 80°C for 5+ minutes | Warning / Critical | Ticket + Alert |
| Chassis Intrusion | Any trigger | Critical | Immediate Page |
| Fan Failure | Any trigger | Critical | Ticket + Alert |
| BIOS/Firmware Change | Any unauthorized change | Critical | Immediate Page |
| Voltage Out of Range | > 10% deviation | Warning | Ticket |
| Power Cycle (unplanned) | Any off-schedule | Warning | Ticket |
Best Practices and Common Pitfalls
Do
- Integrate PET with your SIEM from day one. Standalone trap logging to a syslog file provides little operational value.
- Keep BMC firmware updated. Outdated firmware is the most common source of malformed or missing traps.
- Test your alert pipeline monthly. Send a deliberate test trap (most BMC interfaces have a “send test trap” function) and verify end-to-end delivery to your SIEM and on-call system.
- Isolate the BMC management network on a dedicated VLAN, separate from server production traffic. Exposing BMC interfaces to the general network is a critical security vulnerability.
- Use SNMPv3 with authPriv security level in all production environments.
- Document all Event IDs and OIDs used in your environment in a central runbook. This dramatically reduces mean-time-to-diagnose during incidents.
Don’t
- Don’t ignore “Info” severity PET alerts. They often precede failures by hours or days and are valuable for predictive maintenance.
- Don’t leave PET on the default community string (“public”). This is equivalent to leaving a door unlocked.
- Don’t configure a single management console as the sole trap destination without redundancy. If your trap aggregator is down, your hardware monitoring is blind.
- Don’t skip threshold tuning after initial deployment. Default thresholds are conservative and will generate excessive alert volume in typical data center conditions.
Glossary of Key Terms
| Term | Definition |
| IPMI | Intelligent Platform Management Interface a standardized interface for out-of-band server management. |
| BMC | Baseboard Management Controller a dedicated microcontroller on the server motherboard that runs independently of the main OS. |
| SNMP Trap | An unsolicited notification sent by a network device to a management station when an event occurs. |
| OID | Object Identifier a globally unique identifier in the SNMP MIB tree that classifies the type of event or data. |
| Varbind | Variable Binding a key-value pair within an SNMP Trap carrying event metadata. |
| MIB | Management Information Base a database of OIDs that defines the structure of SNMP data for a device. |
| ASF | Alert Standard Format a DMTF standard defining PET and other pre-OS management alert mechanisms. |
| Community String | A password-like token used in SNMPv1/v2c for basic authentication. |
| Trapd | A trap aggregator daemon (e.g., Oracle’s implementation) that receives, filters, and forwards SNMP traps. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between a Platform Event Trap and a syslog?
A syslog is a software-based log generated and transmitted by the operating system. A PET is a hardware/firmware-based alert sent via IPMI and SNMP by the BMC, completely independent of OS state. If the OS is crashed, compromised, or shut down, syslog stops working PET does not.
Q: Are Platform Event Traps delivered in real time?
Yes. PETs are designed for near-real-time delivery via UDP. There is no connection setup or acknowledgment overhead, which means hardware events are reported within seconds of occurring. The trade-off is that UDP provides no delivery guarantee traps can be dropped on congested networks. For critical environments, the trap aggregator should be on a low-latency, dedicated management network.
Q: What UDP port do SNMP traps use?
SNMP Traps are sent to UDP port 162 on the management console. The sending device (the BMC) uses a random ephemeral source port. Ensure port 162 is open inbound on the trap aggregator’s firewall and that the dedicated management VLAN allows this traffic.
Q: Can a Platform Event Trap stop ransomware?
No PET is a detection and alerting mechanism, not a prevention control. It cannot block an attack. However, it can detect the hardware-level conditions associated with an attack (firmware modification, anomalous CPU load, unexpected reboot) significantly earlier than traditional software-based detection, enabling faster manual response or automated playbook execution via SOAR integration.
Q: How do I find the correct Trap Event ID for my platform?
Event IDs are vendor-specific. On Cisco SONiC platforms, event IDs are defined in the SDK (e.g., LA_EVENT_IPV4_NON_COMP_MC = 0x44) and referenced via the CLI. On Huawei platforms, the event list is documented in the device’s MIB files. On Intel/Oracle platforms, the ASF specification and BMC documentation provide the full OID tree. Always consult your vendor’s MIB documentation and import vendor MIBs into your SNMP management platform for human-readable trap descriptions.
Conclusion
Platform Event Traps occupy a unique and underutilized position in the modern security stack. They operate where attackers increasingly focus below the OS, at the firmware and hardware level and they deliver alerts that no software-based tool can replicate. Whether you are an SRE trying to get ahead of hardware failures, a network engineer building a resilient monitoring pipeline, or a security architect closing the gap between physical security and the SOC, PET deserves a place in your strategy.
The barrier to entry is lower than most engineers expect: enable PET in BIOS, configure SNMPv3 on the BMC, route traps to an aggregator, and connect it to your SIEM. The hard work and the real value comes from tuning thresholds, normalizing data, and building correlation rules that turn hardware events into high-confidence security signals. Done well, a mature PET deployment can detect firmware-level attacks days before an adversary completes their objective.
In a threat landscape where attackers are increasingly “living off the land” below the OS boundary, the organizations that monitor below that boundary will have a decisive advantage.
TECH
Your Screen Is Being Observed on Mac: What It Means & How to Fix It (2026 Guide)
Your Screen Is Being Observed on Mac If you’ve seen the “Your screen is being observed” message on your Mac, you’re not alone. This security alert can be alarming, especially if you weren’t expecting it. Don’t panic — this message doesn’t always mean something sinister is happening. In most cases, it’s triggered by legitimate features like screen sharing or recording apps. However, in rare situations, it could indicate malware or unauthorized remote access.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand what causes this alert, how to identify whether it’s harmless or dangerous, and provide step-by-step instructions to fix it and secure your Mac.
Quick Reference: Common Causes & Fixes
| Cause | Quick Fix |
| Screen Sharing/Remote Management | System Settings > General > Sharing > Disable all sharing options |
| AirPlay Mirroring | Control Center > Screen Mirroring > Turn off AirPlay |
| Screen Recording Apps (Zoom, OBS, QuickTime) | Quit the recording/meeting application |
| Accessibility Features (Zoom, Switch Control) | System Settings > Accessibility > Disable active features |
| Malware/Spyware | Disconnect Wi-Fi, run malware scan, quarantine threats |
What Does “Your Screen Is Being Observed” Mean on a Mac?
This is a privacy and security alert built into macOS. It appears when an application or process has been granted permission to record or view your display. Apple introduced this feature to give users transparency about what’s accessing their screen.
which application is watching, which is why diagnosing the cause requires some investigation.
The core message is this: something on your Mac currently has control over your screen or is recording it. This could be completely legitimate, like when you’re using Zoom for a meeting, or it could signal a security issue like malware or unauthorized remote access.
Common (Harmless) Reasons for This Message
In most cases, this alert is triggered by benign causes — features or apps you’ve intentionally activated. Here are the most common legitimate reasons:
Screen Sharing or Remote Management is Enabled
macOS includes built-in screen sharing and remote management features found in System Settings > General > Sharing. If these are turned on, someone else may be able to view or control your screen remotely.
This is particularly common on work devices managed by IT departments. If your Mac is enrolled in Remote Management or Mobile Device Management (MDM), your employer may have legitimate access to monitor activity for security or compliance purposes. If you’re seeing this on a work device, check with your IT department before disabling anything.

AirPlay Mirroring is Active
If you’re using AirPlay to mirror your Mac’s display to an external monitor, Apple TV, or smart TV, macOS will show the “screen being observed” alert. This is normal — AirPlay requires screen recording permissions to function.
You can check if AirPlay is active by looking at Control Center. If you see a display mirroring icon or an active AirPlay connection, this is the likely cause.
A Screen Recording or Meeting App is Running
Applications that record your screen will trigger this alert. Common examples include:
- QuickTime Player (when recording the screen)
- OBS Studio (streaming and recording software)
- Zoom, Microsoft Teams, or Google Meet (during screen sharing)
- ScreenFlow, Camtasia, or other video production tools
- DisplayLink software (for external USB monitors)
If you recently started or joined a video call and enabled screen sharing, that’s almost certainly why you’re seeing the message. Simply quitting the application should make the alert disappear.
Accessibility Features Are in Use
macOS Accessibility features require screen recording permissions to work properly. These include:
- Zoom (the screen magnification tool, not the meeting app)
- Switch Control (assistive access for physical disabilities)
- VoiceOver with certain settings
- Screen Curtain (privacy feature that blacks out the display)
You can review which accessibility features are active by going to System Settings > Accessibility. If you’re not actively using any assistive technologies, these should all be turned off.
When It Could Be a Serious Problem: Signs of Malware
While most instances of this alert are harmless, there are scenarios where it signals a genuine security threat. Malware, spyware, and Remote Access Trojans (RATs) can gain screen recording permissions without your knowledge, allowing hackers to monitor your activity, steal sensitive information, or even watch you through your webcam.
Common infection vectors include downloading cracked software, clicking malicious links in phishing emails, or installing fake software updates from untrusted websites. Once installed, malicious processes can run silently in the background, giving attackers ongoing surveillance capabilities.
Red Flags That Point to Malware
Pay attention to these warning signs:
- You didn’t enable any of the legitimate features mentioned above — If you’re not using screen sharing, AirPlay, or any recording apps, and the alert persists, investigate immediately.
- Your Mac is behaving strangely — Slow performance, unexpected crashes, unfamiliar applications launching at startup, or high CPU usage from unknown processes.
- The alert appears on the lock screen without explanation — If your Mac is locked and you see this message even though no apps should be running, that’s a major red flag.
- You recently installed software from an untrusted source — Pirated apps, free trials from sketchy websites, or software downloaded outside the Mac App Store can contain hidden malware.
- The message persists after disabling all known features — If you’ve turned off screen sharing, quit all apps, and the alert is still active, it’s time to scan for threats.
If any of these apply to you, proceed directly to the malware scanning step in the troubleshooting guide below. Don’t ignore these signs — addressing them quickly can protect your privacy and prevent data theft.
How to Fix “Your Screen Is Being Observed” — Step-by-Step Guide
Follow these steps in order. Start with the simplest solutions and work your way toward more advanced troubleshooting if needed. Most users will resolve the issue within the first two steps.
Step 1: Check and Disable Legitimate Features
Disable Screen Sharing and Remote Management:
- Open System Settings (click the Apple menu > System Settings)
- Go to General > Sharing
- Turn off Screen Sharing, Remote Management, and Remote Apple Events
- Also check AirDrop & Handoff settings and disable if not in use
Turn Off AirPlay Receiver:
- Click Control Center in the menu bar
- Look for Screen Mirroring or AirPlay Display
- If active, click it and select “Disconnect” or “Turn Off AirPlay”
Quit Screen Recording or Meeting Apps:
- Check if QuickTime, OBS, Zoom, Teams, or similar apps are running
- Fully quit these applications (don’t just minimize — use Cmd+Q or right-click > Quit)
After completing these actions, check if the alert disappears. If it does, you’ve identified the cause. If not, continue to Step 2.
Step 2: Review Accessibility Permissions and Login Items
Check Accessibility Features:
- Go to System Settings > Accessibility
- Review features like Zoom, Switch Control, and Pointer Control
- Disable any that you’re not actively using
Check Login Items (Apps That Start Automatically):
- Go to System Settings > General > Login Items
- Look for unfamiliar applications or background processes
- Remove anything you don’t recognize by clicking the minus (–) button
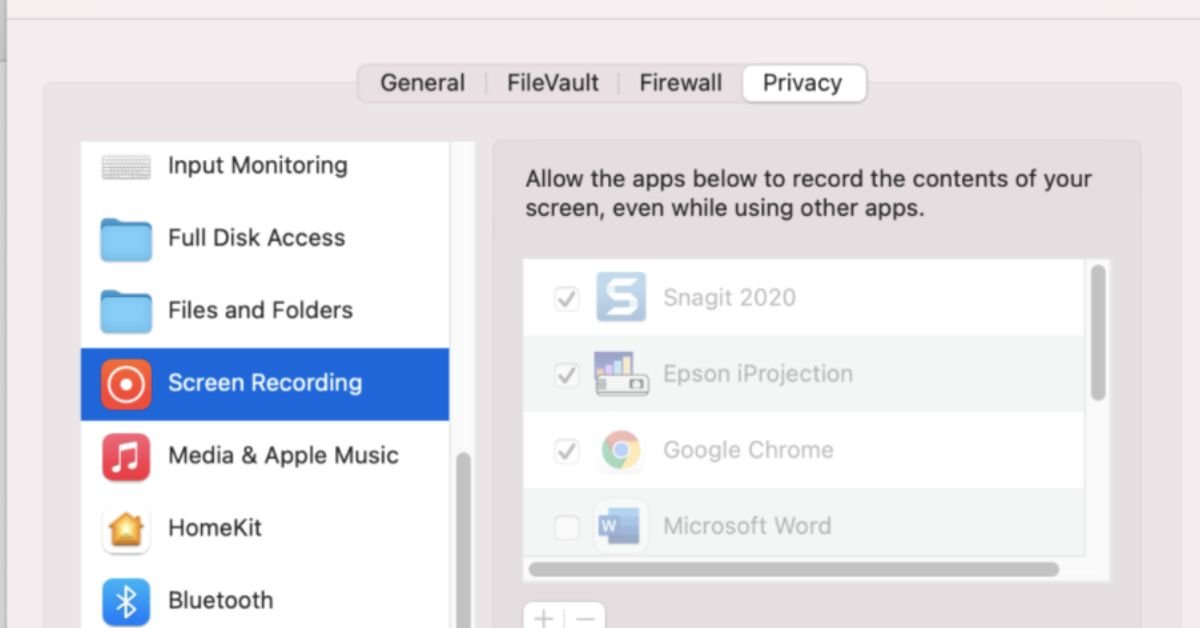
Review Screen Recording Permissions:
- Go to System Settings > Privacy & Security > Screen Recording
- Check which apps have permission to record your screen
- Revoke permissions for any apps you don’t use or recognize
If the alert persists after these checks, it’s time to investigate potential malware.
Step 3: Scan for Malware (Critical Security Step)
If none of the above solutions worked, you may have malware or spyware on your Mac. This is the most important step for protecting your security and peace of mind.
First, disconnect from the internet: This prevents malware from communicating with remote servers or receiving commands from attackers. Turn off Wi-Fi and unplug any Ethernet cables.
Run a deep malware scan: Use reputable Mac security software with real-time protection and deep scanning capabilities. Look for tools that offer:
- Full system scanning (not just quick scans)
- Detection of Remote Access Trojans (RATs) and spyware
- Automatic quarantine of threats
- Real-time monitoring to prevent future infections
If threats are detected: Follow the software’s instructions to quarantine or remove them. After removal, restart your Mac and check if the alert is gone.
Change your passwords: If malware was found, assume your login credentials may have been compromised. Update passwords for your Mac user account, email, banking, and other sensitive accounts immediately.
Step 4: Advanced Troubleshooting and Final Steps
If the issue still isn’t resolved after malware scanning, try these final troubleshooting steps:
Restart your Mac: Sometimes system processes get stuck. A simple restart can clear temporary glitches causing false alerts.
Update macOS: Go to System Settings > General > Software Update and install any available updates. Apple frequently patches security vulnerabilities and system bugs.
Reset SMC and NVRAM (for persistent issues): These low-level resets can fix hardware-related problems. Instructions vary by Mac model — consult Apple’s support documentation for your specific device.
Contact Apple Support: If nothing works, reach out to Apple Support for professional assistance. They can run diagnostics and help identify issues that aren’t user-serviceable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Does this message mean I’m definitely being hacked?
No, not necessarily. In the vast majority of cases, this alert is triggered by legitimate features like screen sharing, AirPlay, or apps you’re actively using. However, if you see this message and can’t identify any legitimate cause after reviewing the common reasons listed in this guide, it’s worth investigating further for malware. The key is to systematically check for known causes before assuming the worst.
Q2: How do I permanently stop this message from appearing?
Ensure that no screen recording features are left enabled when you’re not actively using them. Specifically:
- Keep Screen Sharing and Remote Management disabled unless needed
- Turn off AirPlay when not mirroring to external displays
- Fully quit recording apps after use (don’t just minimize them)
- Review Login Items and remove unnecessary startup applications
- Keep macOS updated to benefit from Apple’s security improvements
By maintaining good security hygiene and being intentional about which apps have screen recording permissions, you can prevent false alerts and ensure the message only appears when it should.
Q3: My work Mac says this. Can I turn it off?
If you’re using a company-issued Mac, this message may be caused by Remote Management or Mobile Device Management (MDM) software installed by your IT department. This is a standard security and compliance measure that allows employers to monitor devices for policy enforcement, troubleshooting, and protection against data breaches.
not attempt to disable it without permission. Doing so could violate company policy and may trigger security alerts. Instead, speak with your IT department to confirm whether the monitoring is intentional and legitimate. They can explain what level of access they have and address any privacy concerns.
Q4: I’ve fixed it, but how do I prevent it from happening again?
Prevention is all about safe computing habits and proactive security measures:
- Only download software from trusted sources: Stick to the Mac App Store or verified developer websites. Avoid pirated software and free trial offers from sketchy sites.
- Be cautious with email attachments and links: Phishing emails are a common malware delivery method. Don’t click links or download files unless you’re certain they’re legitimate.
- Keep your Mac updated: Install macOS updates promptly to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Review app permissions regularly: Periodically check System Settings > Privacy & Security > Screen Recording to ensure only trusted apps have access.
- Use reputable security software: Consider installing anti-malware protection with real-time scanning.
By following these practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of malware infections and protect your privacy and security long-term.
Final Thoughts: Peace of Mind and Protection
Seeing the “Your screen is being observed” message can be unsettling, but in most cases, it’s nothing to worry about. The alert is designed to give you transparency — Apple wants you to know when something is accessing your display, whether it’s a legitimate tool you’re using or a potential threat.
By systematically working through the troubleshooting steps in this guide, you can identify the cause, remove any threats, and secure your Mac against future issues. Remember that knowledge is your best defense — understanding how screen recording permissions work and which apps legitimately need them puts you in control of your privacy and security.

 SCIENCE8 months ago
SCIENCE8 months agoThe Baby Alien Fan Bus Chronicles

 BUSINESS8 months ago
BUSINESS8 months agoMastering the Art of Navigating Business Challenges and Risks

 WORLD6 months ago
WORLD6 months agoMoney Heist Season 6: Release Date, Cast & Plot

 BUSINESS5 months ago
BUSINESS5 months agoTop Insights from FintechZoom.com Bitcoin Reports

 BUSINESS8 months ago
BUSINESS8 months agoNewport News Shipbuilding Furloughs Hit Salaried Workers

 WORLD8 months ago
WORLD8 months agoRainborne Royals: The Rise of Winged Termites

 WORLD8 months ago
WORLD8 months agoRainwalkers: The Secret Life of Worms in the Wet

 FOOD8 months ago
FOOD8 months agoBFC Monster Energy: Legendary Power Can Shocks Fans – 32
















