TECH
Unlocking the Power of Titanium: A Deep Dive into its Versatility

Unlocking the Power of Titanium is often heralded as one of the most powerful metals in the world, known for its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional resistance to corrosion. From aerospace engineering to medical applications, titanium’s versatility makes it a material of choice in industries ranging from manufacturing to biotechnology. This article delves into the many applications of titanium, exploring why it’s considered a material of the future, and how it has revolutionized various sectors.
The Composition and Unique Properties of Titanium
Titanium is a transition metal that belongs to the periodic table’s group 4, with an atomic number of 22. It is not just about its physical appearance, which is typically silvery-white, but also its amazing physical properties that make it stand out. Titanium alloys, particularly those composed of titanium, aluminum, and vanadium, are incredibly strong yet lightweight. This unique strength-to-weight ratio makes titanium alloys indispensable in industries that demand both resilience and lightness.

High Strength and Durability
One of titanium’s most celebrated features is its superior strength-to-weight ratio. Compared to steel, titanium is just as strong but about 45% lighter. This makes it an ideal material for use in high-performance applications where weight is a concern. For instance, titanium is used extensively in aerospace, including aircraft and spacecraft, to reduce fuel consumption and increase efficiency. The aerospace industry benefits from titanium’s ability to withstand extreme temperatures and high stress without compromising its integrity.
Exceptional Corrosion Resistance
Another reason for titanium’s widespread use is its exceptional corrosion resistance. It forms a protective oxide layer when exposed to air, preventing rust and decay. This makes titanium an excellent choice for use in harsh environments, including marine settings, where corrosion can be a significant issue. Titanium’s resistance to saltwater, chemicals, and even chlorides makes it indispensable in industries like desalination and offshore drilling.
Titanium in the Aerospace Industry
In the world of aerospace engineering, titanium has long been a game-changer. Its high strength and resistance to corrosion have made it the material of choice for everything from military aircraft to commercial airliners. When designing aircraft, engineers need materials that are both lightweight and capable of enduring intense pressures and temperature fluctuations. Titanium’s ability to perform under such conditions ensures that it plays a vital role in the performance and longevity of air and spacecraft.
Titanium Components in Aircraft and Spacecraft
Titanium alloys are used in a variety of parts, including turbine blades, engine components, and structural elements. The aerospace sector relies on titanium’s ability to withstand extreme temperatures while maintaining its integrity. For example, the Boeing 787 Dreamliner and the Airbus A350 both make use of titanium in their construction, reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency.
In addition, the use of titanium in spacecraft, such as NASA’s Mars Rovers, has been critical to the success of space exploration. Titanium’s strength and lightness allow space vehicles to carry more payload and endure the harsh environment of space.
Titanium in the Medical Field
Titanium is also making significant strides in the medical and healthcare sectors. Its biocompatibility—meaning it does not cause adverse reactions when introduced into the body—makes it an ideal material for implants and prosthetics. Medical devices like joint replacements, dental implants, and even pacemakers often incorporate titanium.
Titanium as an Implant Material
When it comes to joint replacements, titanium is favored because it can bond with bone tissue, a process known as osseointegration. This makes titanium implants more stable and effective than those made from other materials. Its non-reactive nature ensures that titanium does not cause inflammation or infection, leading to a smoother recovery process for patients.
Dental Implants Made from Titanium
Titanium has revolutionized the field of dentistry by enabling the development of dental implants that mimic the function of natural teeth. Since titanium naturally integrates with bone tissue, dental implants made from this metal are incredibly durable, allowing patients to restore their smile with confidence.
Advancements in Titanium Medical Devices
Beyond implants, titanium is also widely used in the creation of surgical tools, prosthetics, and even in some cutting-edge cancer treatments. Researchers are exploring the use of titanium in radiation therapy to create more precise and targeted treatments that minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Titanium in the Automotive Industry
Though less discussed, titanium’s impact on the automotive industry is undeniable. Car manufacturers are increasingly turning to titanium to enhance vehicle performance and reduce overall weight. Whether it’s for high-performance sports cars or luxury vehicles, titanium’s strength and weight-saving properties are a game-changer in automotive design.
Titanium in Car Engines and Exhaust Systems
The automotive industry uses titanium in engine components, such as pistons and connecting rods, due to its strength and ability to withstand high temperatures. Additionally, titanium’s resistance to corrosion makes it an excellent choice for exhaust systems. The use of titanium in automotive exhaust systems helps to improve the longevity and efficiency of the vehicle, reducing the frequency of replacements and improving performance.
Titanium Components in Luxury and Sports Cars
Luxury and performance car manufacturers like Ferrari and Lamborghini use titanium for various parts of their vehicles, such as suspension components and brake systems. The result is a vehicle that not only performs better but also has a more stylish and exclusive look.
Future Innovations in Titanium Technology
As research and technology continue to evolve, new uses for titanium are emerging. The demand for titanium is expected to rise as industries, especially in the fields of renewable energy, robotics, and defense, find new ways to harness its properties.

Titanium and the Future of Renewable Energy
The renewable energy sector is one area where titanium’s unique properties are beginning to shine. Titanium is used in solar panels, wind turbines, and hydrogen storage, thanks to its ability to resist corrosion in harsh outdoor environments. As the world shifts towards renewable energy, titanium will likely play an increasingly vital role in the development of energy-efficient solutions.
Titanium in Robotics and Advanced Manufacturing
The rise of robotics and 3D printing is opening new doors for titanium’s application. Titanium alloys are ideal for creating lightweight, yet strong, robotic parts and components, making them perfect for industries ranging from healthcare to manufacturing.
FAQs About Titanium
Why is titanium considered one of the strongest metals?
Titanium’s strength comes from its unique crystalline structure, which allows it to resist deformation under stress. Additionally, it is about 45% lighter than steel while maintaining a similar strength, making it one of the strongest materials available.
How does titanium benefit the aerospace industry?
Titanium’s high strength-to-weight ratio, resistance to corrosion, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures make it an essential material in the aerospace industry. It is used in aircraft and spacecraft components, improving fuel efficiency and overall performance.
What are the advantages of titanium implants in the medical field?
Titanium is biocompatible, meaning it can integrate seamlessly with human bone tissue without causing adverse reactions. This makes it the material of choice for implants, including dental implants and joint replacements.
Can titanium be used in everyday products?
Yes, titanium is used in everyday products such as watches, eyeglass frames, and even sporting equipment due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion.
What is the cost of titanium?
Titanium is more expensive than common metals like steel, primarily due to its extraction process and the cost of refining it. However, its durability and unique properties justify the price in specialized applications.
Conclusion
Titanium’s exceptional properties—strength, lightweight, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility—make it one of the most versatile and invaluable materials in modern industry. Whether it’s revolutionizing the aerospace sector, enhancing medical implants, or powering the automotive industry, titanium is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. As technology continues to advance, so too will the applications for titanium, cementing its place as a material for the future.
TECH
Your Screen Is Being Observed on Mac: What It Means & How to Fix It (2026 Guide)
Your Screen Is Being Observed on Mac If you’ve seen the “Your screen is being observed” message on your Mac, you’re not alone. This security alert can be alarming, especially if you weren’t expecting it. Don’t panic — this message doesn’t always mean something sinister is happening. In most cases, it’s triggered by legitimate features like screen sharing or recording apps. However, in rare situations, it could indicate malware or unauthorized remote access.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand what causes this alert, how to identify whether it’s harmless or dangerous, and provide step-by-step instructions to fix it and secure your Mac.
Quick Reference: Common Causes & Fixes
| Cause | Quick Fix |
| Screen Sharing/Remote Management | System Settings > General > Sharing > Disable all sharing options |
| AirPlay Mirroring | Control Center > Screen Mirroring > Turn off AirPlay |
| Screen Recording Apps (Zoom, OBS, QuickTime) | Quit the recording/meeting application |
| Accessibility Features (Zoom, Switch Control) | System Settings > Accessibility > Disable active features |
| Malware/Spyware | Disconnect Wi-Fi, run malware scan, quarantine threats |
What Does “Your Screen Is Being Observed” Mean on a Mac?
This is a privacy and security alert built into macOS. It appears when an application or process has been granted permission to record or view your display. Apple introduced this feature to give users transparency about what’s accessing their screen.
which application is watching, which is why diagnosing the cause requires some investigation.
The core message is this: something on your Mac currently has control over your screen or is recording it. This could be completely legitimate, like when you’re using Zoom for a meeting, or it could signal a security issue like malware or unauthorized remote access.
Common (Harmless) Reasons for This Message
In most cases, this alert is triggered by benign causes — features or apps you’ve intentionally activated. Here are the most common legitimate reasons:
Screen Sharing or Remote Management is Enabled
macOS includes built-in screen sharing and remote management features found in System Settings > General > Sharing. If these are turned on, someone else may be able to view or control your screen remotely.
This is particularly common on work devices managed by IT departments. If your Mac is enrolled in Remote Management or Mobile Device Management (MDM), your employer may have legitimate access to monitor activity for security or compliance purposes. If you’re seeing this on a work device, check with your IT department before disabling anything.

AirPlay Mirroring is Active
If you’re using AirPlay to mirror your Mac’s display to an external monitor, Apple TV, or smart TV, macOS will show the “screen being observed” alert. This is normal — AirPlay requires screen recording permissions to function.
You can check if AirPlay is active by looking at Control Center. If you see a display mirroring icon or an active AirPlay connection, this is the likely cause.
A Screen Recording or Meeting App is Running
Applications that record your screen will trigger this alert. Common examples include:
- QuickTime Player (when recording the screen)
- OBS Studio (streaming and recording software)
- Zoom, Microsoft Teams, or Google Meet (during screen sharing)
- ScreenFlow, Camtasia, or other video production tools
- DisplayLink software (for external USB monitors)
If you recently started or joined a video call and enabled screen sharing, that’s almost certainly why you’re seeing the message. Simply quitting the application should make the alert disappear.
Accessibility Features Are in Use
macOS Accessibility features require screen recording permissions to work properly. These include:
- Zoom (the screen magnification tool, not the meeting app)
- Switch Control (assistive access for physical disabilities)
- VoiceOver with certain settings
- Screen Curtain (privacy feature that blacks out the display)
You can review which accessibility features are active by going to System Settings > Accessibility. If you’re not actively using any assistive technologies, these should all be turned off.
When It Could Be a Serious Problem: Signs of Malware
While most instances of this alert are harmless, there are scenarios where it signals a genuine security threat. Malware, spyware, and Remote Access Trojans (RATs) can gain screen recording permissions without your knowledge, allowing hackers to monitor your activity, steal sensitive information, or even watch you through your webcam.
Common infection vectors include downloading cracked software, clicking malicious links in phishing emails, or installing fake software updates from untrusted websites. Once installed, malicious processes can run silently in the background, giving attackers ongoing surveillance capabilities.
Red Flags That Point to Malware
Pay attention to these warning signs:
- You didn’t enable any of the legitimate features mentioned above — If you’re not using screen sharing, AirPlay, or any recording apps, and the alert persists, investigate immediately.
- Your Mac is behaving strangely — Slow performance, unexpected crashes, unfamiliar applications launching at startup, or high CPU usage from unknown processes.
- The alert appears on the lock screen without explanation — If your Mac is locked and you see this message even though no apps should be running, that’s a major red flag.
- You recently installed software from an untrusted source — Pirated apps, free trials from sketchy websites, or software downloaded outside the Mac App Store can contain hidden malware.
- The message persists after disabling all known features — If you’ve turned off screen sharing, quit all apps, and the alert is still active, it’s time to scan for threats.
If any of these apply to you, proceed directly to the malware scanning step in the troubleshooting guide below. Don’t ignore these signs — addressing them quickly can protect your privacy and prevent data theft.
How to Fix “Your Screen Is Being Observed” — Step-by-Step Guide
Follow these steps in order. Start with the simplest solutions and work your way toward more advanced troubleshooting if needed. Most users will resolve the issue within the first two steps.
Step 1: Check and Disable Legitimate Features
Disable Screen Sharing and Remote Management:
- Open System Settings (click the Apple menu > System Settings)
- Go to General > Sharing
- Turn off Screen Sharing, Remote Management, and Remote Apple Events
- Also check AirDrop & Handoff settings and disable if not in use
Turn Off AirPlay Receiver:
- Click Control Center in the menu bar
- Look for Screen Mirroring or AirPlay Display
- If active, click it and select “Disconnect” or “Turn Off AirPlay”
Quit Screen Recording or Meeting Apps:
- Check if QuickTime, OBS, Zoom, Teams, or similar apps are running
- Fully quit these applications (don’t just minimize — use Cmd+Q or right-click > Quit)
After completing these actions, check if the alert disappears. If it does, you’ve identified the cause. If not, continue to Step 2.
Step 2: Review Accessibility Permissions and Login Items
Check Accessibility Features:
- Go to System Settings > Accessibility
- Review features like Zoom, Switch Control, and Pointer Control
- Disable any that you’re not actively using
Check Login Items (Apps That Start Automatically):
- Go to System Settings > General > Login Items
- Look for unfamiliar applications or background processes
- Remove anything you don’t recognize by clicking the minus (–) button
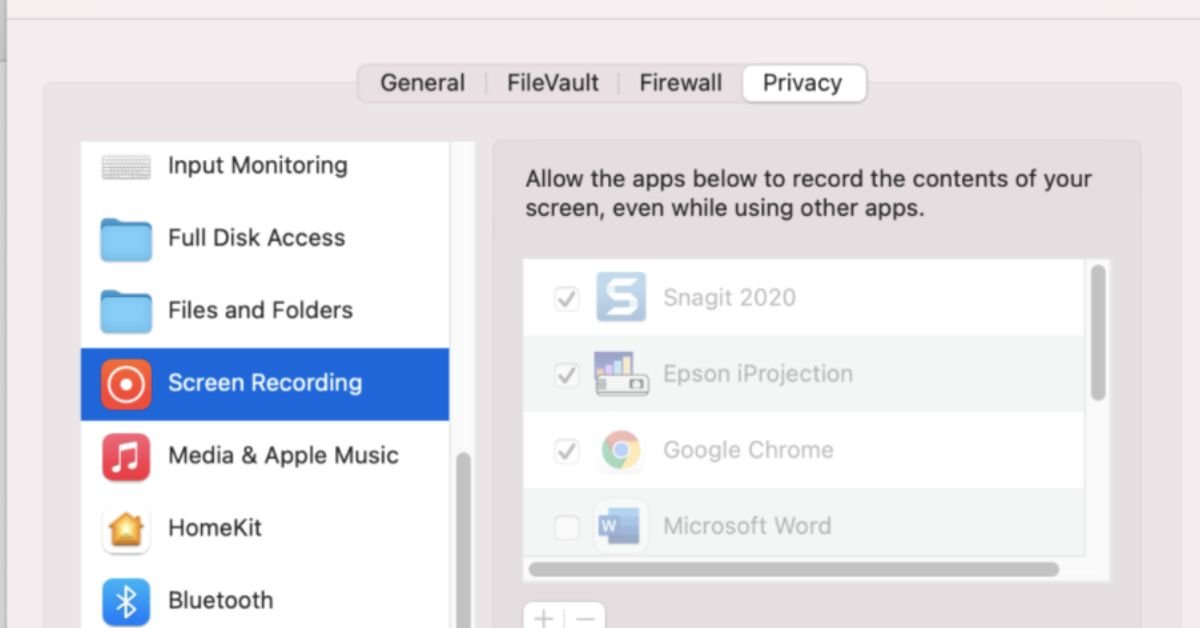
Review Screen Recording Permissions:
- Go to System Settings > Privacy & Security > Screen Recording
- Check which apps have permission to record your screen
- Revoke permissions for any apps you don’t use or recognize
If the alert persists after these checks, it’s time to investigate potential malware.
Step 3: Scan for Malware (Critical Security Step)
If none of the above solutions worked, you may have malware or spyware on your Mac. This is the most important step for protecting your security and peace of mind.
First, disconnect from the internet: This prevents malware from communicating with remote servers or receiving commands from attackers. Turn off Wi-Fi and unplug any Ethernet cables.
Run a deep malware scan: Use reputable Mac security software with real-time protection and deep scanning capabilities. Look for tools that offer:
- Full system scanning (not just quick scans)
- Detection of Remote Access Trojans (RATs) and spyware
- Automatic quarantine of threats
- Real-time monitoring to prevent future infections
If threats are detected: Follow the software’s instructions to quarantine or remove them. After removal, restart your Mac and check if the alert is gone.
Change your passwords: If malware was found, assume your login credentials may have been compromised. Update passwords for your Mac user account, email, banking, and other sensitive accounts immediately.
Step 4: Advanced Troubleshooting and Final Steps
If the issue still isn’t resolved after malware scanning, try these final troubleshooting steps:
Restart your Mac: Sometimes system processes get stuck. A simple restart can clear temporary glitches causing false alerts.
Update macOS: Go to System Settings > General > Software Update and install any available updates. Apple frequently patches security vulnerabilities and system bugs.
Reset SMC and NVRAM (for persistent issues): These low-level resets can fix hardware-related problems. Instructions vary by Mac model — consult Apple’s support documentation for your specific device.
Contact Apple Support: If nothing works, reach out to Apple Support for professional assistance. They can run diagnostics and help identify issues that aren’t user-serviceable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Does this message mean I’m definitely being hacked?
No, not necessarily. In the vast majority of cases, this alert is triggered by legitimate features like screen sharing, AirPlay, or apps you’re actively using. However, if you see this message and can’t identify any legitimate cause after reviewing the common reasons listed in this guide, it’s worth investigating further for malware. The key is to systematically check for known causes before assuming the worst.
Q2: How do I permanently stop this message from appearing?
Ensure that no screen recording features are left enabled when you’re not actively using them. Specifically:
- Keep Screen Sharing and Remote Management disabled unless needed
- Turn off AirPlay when not mirroring to external displays
- Fully quit recording apps after use (don’t just minimize them)
- Review Login Items and remove unnecessary startup applications
- Keep macOS updated to benefit from Apple’s security improvements
By maintaining good security hygiene and being intentional about which apps have screen recording permissions, you can prevent false alerts and ensure the message only appears when it should.
Q3: My work Mac says this. Can I turn it off?
If you’re using a company-issued Mac, this message may be caused by Remote Management or Mobile Device Management (MDM) software installed by your IT department. This is a standard security and compliance measure that allows employers to monitor devices for policy enforcement, troubleshooting, and protection against data breaches.
not attempt to disable it without permission. Doing so could violate company policy and may trigger security alerts. Instead, speak with your IT department to confirm whether the monitoring is intentional and legitimate. They can explain what level of access they have and address any privacy concerns.
Q4: I’ve fixed it, but how do I prevent it from happening again?
Prevention is all about safe computing habits and proactive security measures:
- Only download software from trusted sources: Stick to the Mac App Store or verified developer websites. Avoid pirated software and free trial offers from sketchy sites.
- Be cautious with email attachments and links: Phishing emails are a common malware delivery method. Don’t click links or download files unless you’re certain they’re legitimate.
- Keep your Mac updated: Install macOS updates promptly to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Review app permissions regularly: Periodically check System Settings > Privacy & Security > Screen Recording to ensure only trusted apps have access.
- Use reputable security software: Consider installing anti-malware protection with real-time scanning.
By following these practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of malware infections and protect your privacy and security long-term.
Final Thoughts: Peace of Mind and Protection
Seeing the “Your screen is being observed” message can be unsettling, but in most cases, it’s nothing to worry about. The alert is designed to give you transparency — Apple wants you to know when something is accessing your display, whether it’s a legitimate tool you’re using or a potential threat.
By systematically working through the troubleshooting steps in this guide, you can identify the cause, remove any threats, and secure your Mac against future issues. Remember that knowledge is your best defense — understanding how screen recording permissions work and which apps legitimately need them puts you in control of your privacy and security.
TECH
Gemini 2.5 Pro vs Claude Sonnet 4:The Ultimate 2026 Decision Guide for Developers

Gemini 2.5 Pro vs Claude Sonnet 4 The debate between Gemini 2.5 Pro and Claude Sonnet 4 has become one of the most important decisions for development teams in 2026. While benchmark scores provide valuable insights—with both models scoring impressively on metrics like SWE-bench (Gemini 2.5 Pro at 58.7% and Claude Sonnet 4 at 49.0%)—the reality is that
the best model depends on your specific project type, team workflow, and budget constraints. This comprehensive guide goes beyond surface-level comparisons to help you make a confident, informed decision.
At a Glance: Headline Numbers & Verdict
Key Differentiators Summary
| Feature | Gemini 2.5 Pro | Claude Sonnet 4 |
| SWE-bench Score | 58.7% (state-of-the-art) | 49.0% |
| Context Window | 1 million tokens | 200,000 tokens |
| Input Pricing | $1.00 per 1M tokens | $3.00 per 1M tokens |
| Output Pricing | $10.00 per 1M tokens | $15.00 per 1M tokens |
| Multimodality | Image, video, audio | Image, PDF |
| Ideal Use Case | Large codebases, data science, algorithmic work | Complex refactoring, nuanced understanding, iterative development |
Quick-Verdict Decision Framework
Choose Gemini 2.5 Pro if:
- You’re working with massive codebases (100,000+ lines) that need to fit in a single context window
- Your project involves heavy mathematical, algorithmic, or data science work where benchmark scores matter
- You need multimodal capabilities like debugging from video screen recordings or generating code from visual wireframes
- Budget is a primary concern and you want the most performance per dollar
Choose Claude Sonnet 4 if:
- You’re refactoring or maintaining complex legacy systems that require deep contextual understanding
- Your workflow prioritizes code quality and adherence to architectural patterns over raw speed
- You need a model that requires fewer follow-up prompts and produces more production-ready code on the first attempt
- Developer time is more expensive than API costs in your total cost of ownership calculation
Under the Hood: Specifications & Features Deep Dive
Context Window: 1M Tokens vs. 200K – What It Really Means
The context window difference is one of the most dramatic between these models. Gemini 2.5 Pro’s 1 million token context window means you can ingest an entire large-scale React application—including node_modules, configuration files, and documentation—in a single prompt. For perspective, the entire Harry Potter series fits in about 1.1 million tokens.
Claude Sonnet 4’s 200,000 token window, while still substantial, requires more strategic chunking. For a typical monolithic application with 100,000 lines of code, you’ll need to selectively provide relevant files rather than dumping everything at once. This isn’t necessarily a disadvantage—it forces better prompt engineering and can actually lead to more focused responses.
Real-world impact: When debugging a microservices architecture, Gemini can hold the entire system’s codebase in memory, understanding cross-service dependencies without you needing to manually identify relevant files. Claude requires you to provide the specific services involved, which demands more upfront analysis but often produces more targeted solutions.
Multimodality: Gemini’s Game-Changer for Developers
Gemini 2.5 Pro’s support for image, video, and audio inputs opens up entirely new debugging and development workflows that Claude simply cannot match. Here are concrete use cases that showcase this advantage:
Video-based debugging:
Record your screen showing a UI bug in action—hover states, animation glitches, responsive breakpoints failing—and Gemini can analyze the video to identify the root cause. This eliminates the challenge of describing visual bugs in text, which often loses critical details.
Wireframe-to-code generation:
Sketch your component layout on paper or a whiteboard, photograph it, and Gemini can generate the corresponding React or Vue components with appropriate styling. For rapid prototyping sessions with designers, this significantly accelerates the transition from concept to code.
Documentation from diagrams:
Feed architecture diagrams, database schemas, or flowcharts directly into Gemini for automatic documentation generation or code scaffolding that matches your visual specifications.
Claude Sonnet 4 supports images and PDFs, which is valuable for analyzing screenshots, design mockups, and documentation. However, the lack of video and audio support means certain debugging workflows remain text-dependent.
Thinking Modes Compared: Extended Thinking vs. Deep Think
Both models offer advanced reasoning modes that generate additional tokens to “think through” complex problems before producing their final answer. Understanding how to leverage these modes is critical for getting the best results.

Claude’s Extended Thinking:
Activated by including phrases like “think through this carefully” or “consider multiple approaches” in your prompt, Claude’s extended thinking mode produces visible reasoning chains. You can see the model weighing trade-offs, considering edge cases, and planning its approach before writing code. This transparency is invaluable for learning and verification.
The thinking tokens are billed at the same rate as input tokens ($3/1M), making it relatively affordable to enable. For complex refactoring or architectural decisions, the cost is easily justified by the quality improvement.
Gemini’s Deep Think:
Gemini’s Deep Think mode works similarly but with less visible reasoning. The model internally generates extended reasoning but typically doesn’t expose the full thinking process in the response. You can request it explicitly by setting parameters in your API calls or using prompts that emphasize thorough analysis.
Which to use: For educational purposes or when you need to validate the model’s reasoning, Claude’s transparent thinking is superior. For production systems where you just want the best answer and don’t need to see the work, Gemini’s approach can be more efficient. Both significantly improve performance on complex algorithmic challenges, mathematical proofs, and system design questions.
Performance Face-Off: Benchmarks vs. Real-World Coding
Raw Benchmark Scores
According to independent analysis from Artificial Analysis, Gemini 2.5 Pro currently leads on most intelligence benchmarks that are relevant for coding tasks:
| Benchmark | Gemini 2.5 Pro | Claude Sonnet 4 |
| SWE-bench Verified | 58.7% | 49.0% |
| AIME 2024 | 73.3% | 16.7% |
| LiveCodeBench (Hard) | 54.3% | 45.8% |
These benchmarks test different aspects of coding ability. SWE-bench measures the ability to solve real-world GitHub issues from popular open-source repositories. AIME tests mathematical reasoning, which translates to algorithmic problem-solving. LiveCodeBench evaluates competitive programming skills.
Real-World Coding Test: Methodology and Results
To complement benchmark data with practical insights, we conducted a real-world coding challenge using both models. We chose a representative task: building a collaborative feature management dashboard using Next.js 14, TypeScript, Tailwind CSS, and the Velt SDK for real-time collaboration.
Test Parameters:
- Task: Create a feature flag management interface with real-time presence indicators, inline commenting on flags, and cursor tracking
- Starting point: Blank Next.js 14 project with dependencies installed
- Success criteria: Functional UI with all specified features, production-ready code quality, proper TypeScript typing, responsive design
- Evaluation: We measured completion time, number of follow-up prompts required, code quality (linting, type safety), and bugs discovered in testing
Results Summary:
| Metric | Gemini 2.5 Pro | Claude Sonnet 4 | Winner |
| Initial completion time | 12 minutes | 18 minutes | Gemini |
| Follow-up prompts | 7 | 3 | Claude |
| Bugs discovered | 5 (type errors, null checks) | 1 (minor styling) | Claude |
| API cost | $0.89 | $1.47 | Gemini |
| Developer time (2h) | $200 | $150 | Claude |
| Total Cost of Ownership | $200.89 | $151.47 | Claude |
This Total Cost of Ownership calculation, assuming a developer rate of $100/hour, reveals a critical insight: Claude Sonnet 4’s higher API costs are more than offset by reduced iteration time and fewer bugs. While Gemini completed the initial code faster, the additional debugging and refinement required made it ultimately more expensive in terms of total project cost.
Choosing Your Champion: A Project-Based Framework
Rather than declaring a universal winner, the most practical approach is to select your model based on specific project characteristics. Here’s a comprehensive decision framework:
For Complex System Understanding & Refactoring: Claude Sonnet 4
Claude Sonnet 4 excels when deep contextual understanding matters more than raw speed. If you’re working with a legacy codebase that has evolved over years, with architectural decisions buried in commits from multiple contributors, Claude’s reasoning capabilities shine.
Ideal scenarios:
- Migrating a monolithic Rails application to microservices, where understanding implicit dependencies is crucial
- Refactoring a poorly-documented codebase where you need the model to infer intent from implementation patterns
- Implementing security patches that require understanding how data flows through multiple abstraction layers
- Code reviews where architectural consistency and adherence to established patterns matter
For Large Codebases & Data/Algorithm Work: Gemini 2.5 Pro
Gemini’s massive context window and superior benchmark scores on mathematical reasoning make it the clear choice for projects where scale and algorithmic complexity dominate.
Ideal scenarios:
- Building machine learning pipelines that span data ingestion, feature engineering, model training, and deployment
- Working with massive enterprise codebases (e.g., entire ERP systems) where providing complete context eliminates ambiguity
- Implementing complex algorithms like graph processing, optimization problems, or cryptographic systems
- Budget-conscious projects where lower API costs matter, especially with high token usage
For Rapid Prototyping & UI Development: Consider Both
Frontend development presents an interesting use case where both models have distinct advantages. Gemini’s multimodal capabilities allow it to generate components from visual mockups or screenshots, which is invaluable during the design-to-code phase. Simply upload a Figma screenshot and receive corresponding React components.
However, developer feedback consistently indicates that Claude produces more aesthetically pleasing and modern UI code. It tends to select better color schemes, implement more thoughtful spacing, and create more polished animations without explicit instruction.
Hybrid approach: Use Gemini for initial code generation from designs, then refine with Claude for production polish. This leverages the strengths of both models within a single workflow.
Pricing, Integration & The Developer Workflow
Pricing Model Decoded: Token Costs and Smart Savings
Understanding the pricing structure is essential for budget forecasting. Both models use token-based pricing with separate rates for input (what you send) and output (what the model generates).
Gemini 2.5 Pro:
- Input: $1.00 per 1 million tokens
- Output: $10.00 per 1 million tokens
Claude Sonnet 4:
- Input: $3.00 per 1 million tokens
- Output: $15.00 per 1 million tokens
Real-world cost examples:
For a typical API request with 10,000 input tokens (roughly 7,500 words) and 2,000 output tokens (about 1,500 words), the costs break down as follows:
- Gemini: (10,000 × $0.000001) + (2,000 × $0.00001) = $0.01 + $0.02 = $0.03
- Claude: (10,000 × $0.000003) + (2,000 × $0.000015) = $0.03 + $0.03 = $0.06
Cost optimization strategies: Both platforms offer prompt caching, which stores frequently-used context and dramatically reduces input token costs for repeated use. For a development team running hundreds of queries against the same codebase daily, enabling prompt caching can cut costs by 50-90%.
Fitting Into Your Workflow: IDE, CLI, and Cloud Integration
The best AI coding assistant is one that integrates seamlessly into your existing development workflow. Both models offer multiple integration paths:
VS Code & IDEs:
Claude integrates through multiple VS Code extensions, including Anthropic’s official extension and community tools like Continue.dev. Gemini is available through Google’s Duet AI extension and can be accessed via the Google AI Studio. Both support inline code completion, chat panels, and file context awareness.
Command Line:
Claude offers Claude Code, a specialized CLI tool designed for agentic coding workflows. It can autonomously read files, run tests, and iterate on solutions. Gemini is accessible through the Google Cloud CLI and the generative AI SDK, which provides similar scripting capabilities.
Cloud Platforms:
Gemini has native integration with Google Cloud Platform, making it the natural choice for teams already invested in GCP infrastructure. Claude is cloud-agnostic and can be deployed through AWS Bedrock, Google Cloud’s Vertex AI, or directly through Anthropic’s API.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the main difference between Claude Sonnet 4 and Claude 3.7 Sonnet?
Claude Sonnet 4 represents a significant upgrade over Claude 3.7 Sonnet, particularly in coding and mathematical reasoning. The SWE-bench score improved from approximately 40% to 49%, and the model demonstrates substantially better understanding of complex system architectures. Claude Sonnet 4 also offers improved context following and reduced hallucination rates on technical content.
Is Gemini 2.5 Pro worth it for its context window alone?
For massive codebases (100,000+ lines), absolutely. The ability to provide complete system context eliminates the need for manual file selection and reduces back-and-forth clarification. However, for typical projects under 50,000 lines of code, Claude Sonnet 4’s 200K token window is usually sufficient with strategic prompting. The decision should factor in your specific codebase size and complexity.
Which model is faster for iterative debugging?
Gemini 2.5 Pro typically produces code faster (measured in tokens per second), but Claude Sonnet 4 often requires fewer total iterations to reach production-ready code. If you value raw generation speed, Gemini wins. If you prioritize minimizing total development time including debugging, Claude is usually more efficient. The Total Cost of Ownership calculation should be your primary metric.
Can I use both models together for different tasks?
Absolutely, and this is often the optimal strategy. Many development teams use Gemini for initial scaffolding and data pipeline work where its context window and mathematical strengths dominate, then switch to Claude for refactoring, code review, and production polish where quality matters more than speed. The marginal API cost of using both models is typically negligible compared to developer time savings.
How do the “thinking” modes affect my API bill?
Thinking tokens are billed at input rates ($1 per 1M for Gemini, $3 per 1M for Claude). For a complex architectural problem that generates 5,000 thinking tokens before the actual response, you’d pay an additional $0.005 on Gemini or $0.015 on Claude. Given the quality improvement on complex tasks, this is almost always worthwhile. The cost impact becomes noticeable only at very high volumes (thousands of requests per day).
Conclusion: Making Your Decision
The choice between Gemini 2.5 Pro and Claude Sonnet 4 ultimately depends on your project’s specific requirements, team workflow, and cost structure. Both models represent the state-of-the-art in AI-assisted software development, and neither is universally superior.
Choose Gemini 2.5 Pro if you prioritize context window size, multimodal capabilities, benchmark performance on algorithmic tasks, and lower API costs. It excels at large-scale projects, data science work, and scenarios where you can provide massive amounts of context.
Choose Claude Sonnet 4 if you value code quality over generation speed, need fewer iterations to reach production-ready code, and work with complex systems that require deep understanding. When Total Cost of Ownership includes developer time, Claude often delivers better economic value.
For most development teams, the optimal approach is to evaluate both models with your actual codebase and workflows. Both offer generous free tiers for testing, and the investment of a few hours in comparative evaluation will pay dividends over months of development work. Consider your project characteristics using the framework provided in this guide, and don’t hesitate to use both models for different aspects of your work—the marginal cost is minimal compared to the productivity gains from using the right tool for each task.
TECH
How to Recall an Email in Outlook: Complete 2026 Guide

How to Recall an Email in Outlook Sent an email with a typo, wrong attachment, or to the wrong person? Microsoft Outlook’s recall feature can help. Here’s the quick 4-step process:
- Open your Sent Items folder
- Double-click the email you want to recall
- Click Actions in the Message tab, then select Recall This Message
- Choose to delete unread copies or replace with a corrected message
However, this feature only works under specific conditions. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about recalling emails in Outlook, including platform-specific instructions, common failure reasons, and alternative strategies.
What is Email Recall and When Should You Use It?
Email recall is a Microsoft Outlook feature that allows you to retract messages you’ve already sent—but only if specific conditions are met. When successful, the recall either deletes the unread email from the recipient’s inbox or replaces it with a corrected version.
When Recalling an Email is the Best Option
The recall feature is ideal for these situations:
- You noticed a critical typo or grammatical error immediately after sending
- You forgot to attach an important document
- You sent incorrect information that needs to be corrected
- You accidentally sent the email to the wrong recipient within your organization
- You need to prevent potentially sensitive company information from being read
The key is to act quickly—the longer you wait, the higher the chance the recipient has already opened your message.
Professional Etiquette: Recall vs. Sending a Follow-Up Correction
While email recall is powerful, it’s not always the best approach from a professional standpoint. Consider sending a follow-up correction instead when:
- The error is minor and doesn’t affect the message’s core meaning
- The recipient has likely already read the email
- You’re communicating with external clients or partners (where recall won’t work anyway)
- A transparent acknowledgment of the mistake would build more trust than attempting a recall
A simple follow-up email like “I apologize for the confusion in my previous message. The correct figure is…” often maintains better professional relationships than a failed recall attempt that notifies the recipient you tried to delete something.
How to Recall an Email in Outlook: Step-by-Step
Microsoft has updated Outlook’s interface in recent years, so the exact steps depend on which version you’re using. Below are detailed instructions for both the New Outlook and Classic Outlook for Windows.
For New Outlook (Windows)
Note: The New Outlook interface was rolled out starting in 2023. If you see a toggle switch at the top of your Outlook window that says “Try the new Outlook,” you can switch between versions.
Step 1: Open Your ‘Sent Items’ Folder
In the navigation pane on the left side of Outlook, click on Sent Items. This folder contains all emails you’ve sent from this account.
Step 2: Double-Click to Open the Message
Locate the email you want to recall and double-click it to open it in a new window. The recall feature is only accessible when the message is open in its own window, not in the preview pane.
Step 3: Click ‘Actions’ in the ‘Message’ Tab
At the top of the message window, find the Message tab in the ribbon. Click on the Actions button (it may appear in the “Move” group).
Step 4: Select ‘Recall This Message’
From the dropdown menu that appears, click Recall This Message.
Step 5: Choose ‘Delete unread copies’ or ‘Replace with a new message’
A dialog box will appear with two options:
- Delete unread copies of this message – This option removes the email from recipients’ inboxes if they haven’t opened it yet
- Delete unread copies and replace with a new message – This option deletes the original and lets you send a corrected version (useful when you forgot an attachment or need to fix significant errors)
Pro Tip: Check the box that says Tell me if recall succeeds or fails for each recipient. This ensures you’ll receive a Message Recall Report confirming whether the recall worked.
For Classic Outlook (Windows)
The process is nearly identical in the classic interface, with only minor differences in menu organization:
- Navigate to your Sent Items folder
- Double-click the sent message to open it
- Go to the Message tab or File menu
- Click Actions (or Info in older versions)
- Select Recall This Message
- Choose your recall option and enable success notifications
The Critical Fine Print: When Recalling an Email Will FAIL
Here’s the uncomfortable truth: email recall in Outlook fails more often than it succeeds. Understanding these limitations upfront will save you frustration and help you manage expectations.
6 Conditions That Block Email Recall
The recall will automatically fail if any of the following conditions are true:
1. The Recipient Has Already Opened the Original Email
This is the most common reason for failure. Once a recipient reads your message, it’s too late—the recall cannot remove it. This is why speed is critical. The recall feature only works on unread messages.
2. The Recipient Uses Outlook on the Web (OWA) or Mobile App
Email recall is a client-side feature that requires the recipient to be using Outlook desktop for Windows. If they’re accessing their email through:
- Outlook on the web (formerly Outlook Web Access/OWA)
- Outlook mobile app (iOS or Android)
- Outlook for Mac
- Any third-party email client (Apple Mail, Thunderbird, etc.)
…then the recall will fail. This makes the feature unreliable in modern workplaces where many users access email on multiple devices.

3. The Email Was Sent to an External Address (Outside Your Organization)
Recall only works within your organization’s Microsoft Exchange Server environment. If you sent the email to:
- Gmail, Yahoo, or other external email providers
- A client or partner at a different company
- Your personal email address
…then recall is impossible. The recipient’s email server is completely outside Microsoft’s control.
4. The Recipient’s Mailbox is Managed by a Non-Exchange Server
Even within your organization, if a recipient’s email account is configured with POP3 or IMAP protocols instead of Exchange, the recall won’t work. Both the sender and recipient must be on Microsoft Exchange.
5. A Server-Side Rule Has Moved the Message from the Inbox
If the recipient has set up an email rule that automatically moves messages from you (or with certain subject lines or keywords) to another folder, the recall attempt cannot locate the original message to delete it. The recall mechanism only checks the Inbox.
6. Too Much Time Has Passed
While Microsoft doesn’t specify an official time limit, the practical reality is that the longer you wait, the more likely the recipient has opened the email or accessed it on a non-desktop platform. Act within minutes, not hours, for the best chance of success.
Quick Reference: Recall Success Conditions
| For Recall to Succeed… | Required Condition |
| Email must be unread | ✓ Required |
| Recipient uses Outlook desktop (Windows) | ✓ Required |
| Recipient is within your organization | ✓ Required |
| Both use Microsoft Exchange Server | ✓ Required |
| Email is still in recipient’s Inbox | ✓ Required |
| No server-side rules moved the email | ✓ Required |
Can You Recall an Email in Outlook for Mac, Web, or Mobile?
The short answer: No, the native recall feature is not available on these platforms. However, there are workarounds and alternative strategies you can use.
Outlook for Mac: No Recall, But Try This Workaround
Unfortunately, Microsoft has never implemented the recall feature in Outlook for Mac. If you’re a Mac user who frequently needs to recall emails, your best options are:
- Use Outlook on the Web (see below) for limited “undo send” functionality
- Set up Windows in a virtual machine or Boot Camp to access the Windows version of Outlook when recall is critical
- Use the delay delivery feature (covered below) as a preventive measure
- Contact your IT administrator if you urgently need to recall a message—they may be able to use server-side tools
Reality check: If you regularly work on a Mac, train yourself to use delay delivery or double-check emails before sending. Prevention is more reliable than recall.
Outlook on the Web (New & Classic): Limited “Undo Send”
The web version of Outlook doesn’t have the full recall feature, but it does offer Undo Send—a time-limited option that prevents the email from being sent in the first place.
How it works:
- After you click Send, a notification appears at the top of the screen
- You have a brief window (typically 5-10 seconds) to click Undo
- If you click it in time, the email is stopped and reopens in the compose window
Important limitations:
- This only works for a few seconds after clicking Send
- It’s not the same as recalling an email that’s already been delivered
- Once the undo window closes, the email is sent and cannot be recalled
While less powerful than the desktop recall feature, Undo Send is still useful for catching immediate mistakes. You can adjust the delay time in Outlook on the Web settings (look for “Undo send” in Settings > Mail > Compose and reply).
Outlook Mobile App: How to Delay Sending
The Outlook mobile app (both iOS and Android) does not support email recall. However, you can use scheduled sending to give yourself a review window:
- Compose your email as usual
- Instead of tapping Send, tap the three-dot menu (⋯)
- Select Schedule Send
- Choose a delivery time (e.g., 10 minutes from now)
- If you catch a mistake before the scheduled time, you can cancel or edit the email from your Outbox
This approach is particularly useful for emails you compose on your phone but want to review on your desktop before they’re sent.
Reliable Alternatives to the Native Recall Feature
Given the many limitations of Outlook’s recall feature, it’s wise to have backup strategies. Here are proven alternatives that work across all platforms and email clients.
Use “Delay Delivery” to Give Yourself a Safety Net
The delay delivery feature is one of Outlook’s most underrated tools. It holds your email in the Outbox for a specified period before sending, giving you time to catch mistakes.
How to set up delay delivery (Outlook for Windows):
- Compose your email
- Go to the Options tab
- Click Delay Delivery
- Check Do not deliver before and set a time (e.g., 5 minutes from now)
- Click Send
Pro tip: Set up a rule to automatically delay all emails by 2-5 minutes. Go to File > Manage Rules & Alerts > New Rule > Apply rule on messages I send > defer delivery by a number of minutes.
Why this is better than recall:
- Works for all recipients, internal and external
- No notification to the recipient if you edit or cancel
- Prevents mistakes rather than trying to fix them afterward
While your email sits in the Outbox, you can double-click it to make edits or delete it entirely. Just remember: Outlook must be open and connected to the internet for the delay to work. If you close Outlook, the email will send immediately the next time you open it.
For Highly Sensitive Data: Explore Third-Party Secure Email Solutions
If you regularly send confidential information and need more control, consider enterprise-grade email security tools that offer features beyond Outlook’s capabilities:
- Encrypted email services (e.g., ProtonMail, Virtru) that allow you to revoke access to messages even after delivery
- Data loss prevention (DLP) tools that can block sensitive emails from being sent in the first place
- Secure file-sharing platforms (e.g., SharePoint, Box, Dropbox Business) that let you share links with expiration dates instead of attaching files
These solutions are especially valuable in industries like healthcare, finance, and legal services where email recall failures could result in regulatory violations or data breaches. Consult with your organization’s IT security team to explore enterprise options.
Frequently Asked Questions About Email Recall in Outlook
Q1: Will the recipient know if I try to recall an email?
Yes, in most cases. If the recall fails (which is common), the recipient will receive a notification in their inbox stating that you attempted to recall a message. This can actually draw more attention to your email than if you had simply sent a follow-up correction. The notification says something like: “[Your Name] would like to recall the message.” If the recall succeeds, the recipient typically doesn’t see anything—the email is simply removed from their inbox before they read it.
Q2: How can I tell if my recall was successful?
When you initiate a recall, make sure to check the box labeled “Tell me if recall succeeds or fails for each recipient.” After the recall attempt, you’ll receive a Message Recall Report in your inbox that shows the outcome for each recipient. The report will indicate whether the recall succeeded, failed, or is still pending. If you don’t receive this report, the recall likely failed, or the option wasn’t enabled.
Q3: Is there a time limit for recalling an email?
Microsoft doesn’t specify an official time limit, but the practical answer is: act immediately. The recall only works on unread emails. The longer you wait, the higher the probability that the recipient has already opened your message or accessed it on a platform where recall doesn’t work (like mobile or webmail). For the best chance of success, attempt the recall within minutes of sending—ideally within the first 1-2 minutes.
Q4: What’s the difference between “Delete unread copies” and “Replace with a new message”?
- Delete unread copies: This option simply removes the original email from recipients’ inboxes (if they haven’t read it). Nothing replaces it. Use this when you want to completely retract the message, such as when you sent it to the wrong person.
- Replace with a new message: This option deletes the original email and opens a new compose window where you can send a corrected version. Use this when you forgot an attachment, included wrong information, or need to fix significant errors. The corrected email will be sent to the same recipients.
Both options only work if the original message is unread and all other success conditions are met.
Q5: Can I recall an email sent to a Gmail, Yahoo, or other external address?
Global Entrepreneur Rule Spurs Startup SurgeNo. The recall feature only works for recipients within your organization’s Microsoft Exchange Server environment. Once an email leaves your Exchange server and is delivered to an external email provider (Gmail, Yahoo, AOL, etc.), it’s completely outside Microsoft’s control. You cannot recall emails sent to:
- External clients or partners
- Your personal email accounts
- Anyone using a non-Microsoft email service
In these cases, your only option is to send a follow-up email acknowledging the error and providing the correct information. Some consumer email services (like Gmail) have their own “undo send” features, but these only work for a few seconds after clicking send and don’t interact with Outlook’s recall system at all.
Final Thoughts: Prevention Beats Recall
While Outlook’s email recall feature can be a lifesaver in the right circumstances, it’s far from foolproof. The long list of conditions required for success means you should never rely on it as your primary safety net.
Instead, build these habits:
- Enable delay delivery for all outgoing emails
- Double-check recipients before clicking Send
- Review attachments and links before sending
- Use Outlook’s built-in spelling and grammar checker
- For sensitive emails, draft them and review after a break
When mistakes do happen—and they will—don’t panic. A brief, professional follow-up correction often builds more trust than a failed recall attempt that broadcasts your error. Focus on clear communication and learning from the experience
READ MORE…

 SCIENCE7 months ago
SCIENCE7 months agoThe Baby Alien Fan Bus Chronicles

 BUSINESS8 months ago
BUSINESS8 months agoMastering the Art of Navigating Business Challenges and Risks

 WORLD6 months ago
WORLD6 months agoMoney Heist Season 6: Release Date, Cast & Plot

 BUSINESS5 months ago
BUSINESS5 months agoTop Insights from FintechZoom.com Bitcoin Reports

 WORLD8 months ago
WORLD8 months agoRainwalkers: The Secret Life of Worms in the Wet

 WORLD8 months ago
WORLD8 months agoRainborne Royals: The Rise of Winged Termites

 BUSINESS7 months ago
BUSINESS7 months agoNewport News Shipbuilding Furloughs Hit Salaried Workers

 FOOD7 months ago
FOOD7 months agoBFC Monster Energy: Legendary Power Can Shocks Fans – 32
















